Pancreatitis treaetments
What is Pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, a gland responsible for digestion and blood sugar regulation. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Acute pancreatitis, often severe but usually resolved with medical treatment, can be caused by factors like gallstones, alcohol consumption, infections,
trauma, or high triglycerides. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, rapid pulse, and tender abdomen. Chronic pancreatitis, on the other hand, is a long-term inflammation that can cause permanent damage and scarring. It can result in persistent abdominal pain, digestive problems, weight loss, and diabetes mellitus. Both forms require medical evaluation and management. Treatment for acute pancreatitis involves hospitalization, supportive care, fasting, intravenous fluids, pain management, and addressing underlying causes. Chronic pancreatitis management focuses on pain relief, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, diabetes management, and managing complications.

Causes of Pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Causes:
• Gallstones: Gallstones block the pancreatic duct, causing inflammation and preventing normal digestive enzyme flow.
• Heavy alcohol consumption: Chronic heavy alcohol consumption can irritate and inflame the pancreas, leading to acute or chronic pancreatitis.
• Trauma: Physical trauma to the abdomen can damage the pancreas or disrupt its blood supply.
• Medications: Certain medications like corticosteroids, diuretics, immunosuppressants, and certain antibiotics can increase the risk of pancreatitis.
• High triglycerides: High levels of triglycerides, often seen in conditions like hypertriglyceridemia, can lead to pancreatitis.
• Infections: Viral and bacterial infections can cause inflammation and lead to pancreatitis.
• Genetic factors: Mutations in genes related to pancreatic function and digestive enzyme regulation can increase the risk.
• Autoimmune conditions: The body's immune system can mistakenly attack and inflame the pancreas.
• Pancreatic duct obstruction: Factors like tumors, pancreatic cysts, or pancreatic divisum can block the pancreatic duct.
• Other factors: Hypercalcemia, hyperparathyroidism, cystic fibrosis, and abdominal surgery can increase the risk.
-Pancreatitis Symptoms and Management
• Abdominal pain: Severe, persistent abdominal pain, usually in the upper abdomen, can worsen after eating or lying flat.
• High triglycerides: High levels of triglycerides, often seen in conditions like hypertriglyceridemia, can lead to pancreatitis.
• Infections: Viral and bacterial infections can cause inflammation and lead to pancreatitis.
• Genetic factors: Mutations in genes related to pancreatic function and digestive enzyme regulation can increase the risk.
• Autoimmune conditions: The body's immune system can mistakenly attack and inflame the pancreas.
• Pancreatic duct obstruction: Factors like tumors, pancreatic cysts, or pancreatic divisum can block the pancreatic duct.
• Other factors: Hypercalcemia, hyperparathyroidism, cystic fibrosis, and abdominal surgery can increase the risk.

Features of Pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Symptoms and Management
• Abdominal pain: Severe, persistent abdominal pain, usually in the upper abdomen, can worsen after eating or lying flat.
• Nausea and vomiting: Common symptoms, often accompanied by abdominal discomfort.
• Fever and chills: May occur in cases of acute pancreatitis, especially if there's an infection.
• Rapid pulse: Elevated heart rate, especially in severe cases or dehydration.
• Abdominal tenderness: Tender abdomen, especially in the upper abdomen, may feel bloated or distended.
• Decreased appetite: Common during episodes of acute inflammation.
• Fever and chills: May occur in cases of acute pancreatitis, especially if there's an infection.
• Rapid pulse: Elevated heart rate, especially in severe cases or dehydration.
• Abdominal tenderness: Tender abdomen, especially in the upper abdomen, may feel bloated or distended.
• Decreased appetite: Common during episodes of acute inflammation.
• Jaundice: Yellowing skin and eyes due to bilirubin buildup.
• Changes in bowel movements: Changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea, constipation, or oily stools.
• Tenderness or mass in the abdomen: Palpable mass or area of tenderness in severe cases.
• Shock or organ failure: Complications such as shock, respiratory failure, kidney failure, or multiple organ dysfunction syndrome may occur.
-Pancreatitis Diagnosis Process
• Medical history and physical examination: Inquire about symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, medical history, alcohol consumption, and recent trauma.
• Blood tests: Assess pancreatic enzymes and evaluate for inflammation or organ dysfunction. Elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes indicate pancreatic injury or inflammation.
• Imaging studies: Abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI or MRCP: Visualize pancreas, gallbladder, and surrounding structures.
• Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Involves direct visualization of bile ducts and pancreatic ducts.
• Other tests: Fecal elastase test, genetic testing, or biopsy may be considered.
• Prompt diagnosis and management are essential to prevent complications and improve outcomes. Treatment may include supportive care, pain management, intravenous fluids, nutritional support, and addressing underlying causes.
-Homeopathy and Disease Cure
• Homeopathy is curable, regardless of the duration of illness.
• Early treatment is faster for chronic conditions and later stages.
• Intelligent individuals start treatment as soon as they observe any symptoms.
• Brahm's research-based, scientific treatment module is effective in curing diseases. • A team of qualified doctors systematically observes and analyzes cases. • They record signs, symptoms, disease progression, prognosis, and complications. • They provide detailed disease information, diet charts, exercise plans, and lifestyle plans. • They guide individuals on improving general health conditions through systematic management of homeopathic medicines.
-Pancreatitis Types and Management
1. Acute Pancreatitis: • Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas that can range from mild to severe and life-threatening.
• Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and rapid pulse.
• Changes in bowel movements: Changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea, constipation, or oily stools.
• Tenderness or mass in the abdomen: Palpable mass or area of tenderness in severe cases.
• Shock or organ failure: Complications such as shock, respiratory failure, kidney failure, or multiple organ dysfunction syndrome may occur.
Diagnosis of Pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Diagnosis Process
• Medical history and physical examination: Inquire about symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, medical history, alcohol consumption, and recent trauma.
• Blood tests: Assess pancreatic enzymes and evaluate for inflammation or organ dysfunction. Elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes indicate pancreatic injury or inflammation.
• Imaging studies: Abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, MRI or MRCP: Visualize pancreas, gallbladder, and surrounding structures.
• Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): Involves direct visualization of bile ducts and pancreatic ducts.
• Other tests: Fecal elastase test, genetic testing, or biopsy may be considered.
• Prompt diagnosis and management are essential to prevent complications and improve outcomes. Treatment may include supportive care, pain management, intravenous fluids, nutritional support, and addressing underlying causes.
Treatment for Pancreatitis?
-Homeopathy and Disease Cure
• Homeopathy is curable, regardless of the duration of illness.
• Early treatment is faster for chronic conditions and later stages.
• Intelligent individuals start treatment as soon as they observe any symptoms.
Brahm Homeopathic Healing & Research Centre Treatment Plan
• Brahm's research-based, scientific treatment module is effective in curing diseases. • A team of qualified doctors systematically observes and analyzes cases. • They record signs, symptoms, disease progression, prognosis, and complications. • They provide detailed disease information, diet charts, exercise plans, and lifestyle plans. • They guide individuals on improving general health conditions through systematic management of homeopathic medicines.

Types of pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Types and Management
1. Acute Pancreatitis: • Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas that can range from mild to severe and life-threatening.
• Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and rapid pulse.
• Common causes include gallstones, alcohol consumption, certain medications, infections, high triglyceride levels, and trauma.
• Treatment involves supportive care, fasting to rest the pancreas, intravenous fluids, pain management, and addressing underlying causes.
2. Chronic Pancreatitis: • Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term inflammation of the pancreas characterized by permanent damage and scarring.
• Symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, digestive problems, weight loss, and diabetes mellitus.
• Common causes include long-term alcohol consumption, genetic factors, recurrent acute pancreatitis, autoimmune conditions, and certain medical conditions
. • Treatment focuses on pain relief, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, managing diabetes, and addressing complications.
3. Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis:
• Acute on chronic pancreatitis refers to a flare-up of acute pancreatitis superimposed on a background of chronic pancreatic inflammation.
• It combines features of both acute and chronic pancreatitis, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe depending on the degree of inflammation and underlying pancreatic damage.
4. Calcification Parenchymal:
• Calcification of the pancreatic parenchyma refers to the deposition of calcium salts within the pancreatic tissue. • It can occur in chronic pancreatitis as a result of long-term inflammation and scarring of the pancreas.
5. Intraductal Calculi/Calcification:
• Intraductal calculi or calcifications refer to the presence of calcium deposits within the pancreatic ducts.
• These calcifications can obstruct the flow of pancreatic enzymes and bile, leading to further inflammation and damage to the pancreas
• Treatment involves supportive care, fasting to rest the pancreas, intravenous fluids, pain management, and addressing underlying causes.
2. Chronic Pancreatitis: • Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term inflammation of the pancreas characterized by permanent damage and scarring.
• Symptoms include persistent abdominal pain, digestive problems, weight loss, and diabetes mellitus.
• Common causes include long-term alcohol consumption, genetic factors, recurrent acute pancreatitis, autoimmune conditions, and certain medical conditions
. • Treatment focuses on pain relief, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, managing diabetes, and addressing complications.
3. Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis:
• Acute on chronic pancreatitis refers to a flare-up of acute pancreatitis superimposed on a background of chronic pancreatic inflammation.
• It combines features of both acute and chronic pancreatitis, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe depending on the degree of inflammation and underlying pancreatic damage.
4. Calcification Parenchymal:
• Calcification of the pancreatic parenchyma refers to the deposition of calcium salts within the pancreatic tissue. • It can occur in chronic pancreatitis as a result of long-term inflammation and scarring of the pancreas.
5. Intraductal Calculi/Calcification:
• Intraductal calculi or calcifications refer to the presence of calcium deposits within the pancreatic ducts.
• These calcifications can obstruct the flow of pancreatic enzymes and bile, leading to further inflammation and damage to the pancreas
. 6. Dilated Main Pancreatic Duct:
• Dilatation of the main pancreatic duct refers to an enlargement or widening of the pancreatic duct, which may be seen on imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan
. • It can occur in chronic pancreatitis due to ductal obstruction, scarring, or strictures.
7. Atrophy of Pancreas:
• Atrophy of the pancreas refers to a decrease in the size and volume of pancreatic tissue, often seen in chronic pancreatitis as a result of long-term inflammation and damage.
8. *Necrosis of Pancreas:*
• Pancreatic necrosis occurs when pancreatic tissue dies due to severe inflammation and reduced blood flow. • It is a serious complication of acute pancreatitis and can lead to infection, organ failure, and death if not treated promptly.
9. Pseudocyst of Pancreas/Collection of Fluid:
• A pancreatic pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops in or around the pancreas as a complication of acute or chronic pancreatitis.
• It forms when pancreatic enzymes and fluid leak out of damaged pancreatic tissue and become trapped in surrounding tissue.
10. Peripancreatic Fat Stranding:
• Peripancreatic fat stranding refers to the thickening and increased density of fat tissue around the pancreas, often seen on imaging studies in cases of pancreatitis.
• It results from inflammation and edema of the surrounding tissues.
11. Aneurysm of Arteries Pancreas:
• Aneurysm of pancreatic arteries refers to a bulging or weakening of blood vessels supplying the pancreas, which can occur as a complication of chronic pancreatitis or other vascular diseases.
12. Fistula of Pancreas:
• A pancreatic fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway that forms between the pancreas and other organs or tissues, allowing pancreatic fluid to leak into surrounding areas.
13. Cancer of Pancreas: • Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor that arises from the cells of the pancreas and can be either exocrine or endocrine in origin.
• It is associated with risk factors such as smoking, obesity, family history, chronic pancreatitis, and certain genetic syndromes.
14. Metastasis:
• Metastasis refers to the spread of cancer from its primary site to distant organs or tissues in the body.
• Pancreatic cancer can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and other organs, leading to advanced disease and poorer prognosis. These terms represent various aspects and complications of pancreatitis, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and timely intervention in individuals with pancreatic disorders.
-Pancreatitis Adverse Effects and Treatment
• Chronic pain: Persistent abdominal pain can interfere with daily activities, sleep, and quality of life, leading to physical and emotional distress.
• Malnutrition: Pancreatitis impairs the normal function of the pancreas, leading to malabsorption of nutrients and deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
• Weight loss: Pain and digestive problems can cause unintentional weight loss, exacerbate nutritional deficiencies, and weaken the immune system.
• Diabetes mellitus: Chronic pancreatitis damages insulin-producing cells, leading to impaired insulin secretion and the development of diabetes mellitus.
• Pancreatic pseudocysts: Fluid-filled sacs that develop in or around the pancreas can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and complications.
• Pancreatic insufficiency: The pancreas fails to produce adequate digestive enzymes, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, steatorrhea, bloating, and malnutrition.
• Pancreatic cancer: Chronic inflammation and damage to the pancreas increase the risk of developing pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
• Psychosocial impact: Living with pancreatitis can lead to increased stress, anxiety, depression, social isolation, and reduced quality of life.
• Treatment strategies include pain management, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, diabetes management, lifestyle modifications, and psychological support.

-Homeopathy in Pancreatitis Management
• Homeopathy is a holistic system of medicine that uses highly diluted substances from natural sources to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms.
• Scientific evidence supporting homeopathic remedies for pancreatitis is limited.
• Pancreatitis is a serious medical condition requiring prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention.
Acute Pancreatitis:
• Mild cases may heal within days to weeks with appropriate medical treatment.
• Severe cases may require hospitalization and intensive care, with a longer recovery period. Chronic Pancreatitis: • Long-term condition characterized by permanent damage and scarring of the pancreas.
• Healing time varies depending on the extent of damage, treatment effectiveness, and management of underlying factors.
• Treatment focuses on pain relief, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, managing diabetes, and addressing complications. Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis:
• Individuals experiencing repeated episodes may require ongoing medical management and lifestyle modifications.
. • It can occur in chronic pancreatitis due to ductal obstruction, scarring, or strictures.
7. Atrophy of Pancreas:
• Atrophy of the pancreas refers to a decrease in the size and volume of pancreatic tissue, often seen in chronic pancreatitis as a result of long-term inflammation and damage.
8. *Necrosis of Pancreas:*
• Pancreatic necrosis occurs when pancreatic tissue dies due to severe inflammation and reduced blood flow. • It is a serious complication of acute pancreatitis and can lead to infection, organ failure, and death if not treated promptly.
9. Pseudocyst of Pancreas/Collection of Fluid:
• A pancreatic pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops in or around the pancreas as a complication of acute or chronic pancreatitis.
• It forms when pancreatic enzymes and fluid leak out of damaged pancreatic tissue and become trapped in surrounding tissue.
10. Peripancreatic Fat Stranding:
• Peripancreatic fat stranding refers to the thickening and increased density of fat tissue around the pancreas, often seen on imaging studies in cases of pancreatitis.
• It results from inflammation and edema of the surrounding tissues.
11. Aneurysm of Arteries Pancreas:
• Aneurysm of pancreatic arteries refers to a bulging or weakening of blood vessels supplying the pancreas, which can occur as a complication of chronic pancreatitis or other vascular diseases.
12. Fistula of Pancreas:
• A pancreatic fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway that forms between the pancreas and other organs or tissues, allowing pancreatic fluid to leak into surrounding areas.
13. Cancer of Pancreas: • Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor that arises from the cells of the pancreas and can be either exocrine or endocrine in origin.
• It is associated with risk factors such as smoking, obesity, family history, chronic pancreatitis, and certain genetic syndromes.
14. Metastasis:
• Metastasis refers to the spread of cancer from its primary site to distant organs or tissues in the body.
• Pancreatic cancer can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and other organs, leading to advanced disease and poorer prognosis. These terms represent various aspects and complications of pancreatitis, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and timely intervention in individuals with pancreatic disorders.

Adverse effects of pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Adverse Effects and Treatment
• Chronic pain: Persistent abdominal pain can interfere with daily activities, sleep, and quality of life, leading to physical and emotional distress.
• Malnutrition: Pancreatitis impairs the normal function of the pancreas, leading to malabsorption of nutrients and deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
• Weight loss: Pain and digestive problems can cause unintentional weight loss, exacerbate nutritional deficiencies, and weaken the immune system.
• Diabetes mellitus: Chronic pancreatitis damages insulin-producing cells, leading to impaired insulin secretion and the development of diabetes mellitus.
• Pancreatic pseudocysts: Fluid-filled sacs that develop in or around the pancreas can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and complications.
• Pancreatic insufficiency: The pancreas fails to produce adequate digestive enzymes, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, steatorrhea, bloating, and malnutrition.
• Pancreatic cancer: Chronic inflammation and damage to the pancreas increase the risk of developing pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
• Psychosocial impact: Living with pancreatitis can lead to increased stress, anxiety, depression, social isolation, and reduced quality of life.
• Treatment strategies include pain management, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, diabetes management, lifestyle modifications, and psychological support.
Medicine for pancreatitis?

-Homeopathy in Pancreatitis Management
• Homeopathy is a holistic system of medicine that uses highly diluted substances from natural sources to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms.
• Scientific evidence supporting homeopathic remedies for pancreatitis is limited.
• Pancreatitis is a serious medical condition requiring prompt diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention.
• Homeopathy should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatment.
• Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended to ensure homeopathy complements the overall treatment plan.
• A collaborative approach integrating both conventional and complementary therapies may provide a more comprehensive approach. How long does pancreas take to heal?
• Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended to ensure homeopathy complements the overall treatment plan.
• A collaborative approach integrating both conventional and complementary therapies may provide a more comprehensive approach. How long does pancreas take to heal?
Healing Timeline for Pancreatitis
Acute Pancreatitis:
• Mild cases may heal within days to weeks with appropriate medical treatment.
• Severe cases may require hospitalization and intensive care, with a longer recovery period. Chronic Pancreatitis: • Long-term condition characterized by permanent damage and scarring of the pancreas.
• Healing time varies depending on the extent of damage, treatment effectiveness, and management of underlying factors.
• Treatment focuses on pain relief, nutritional support, enzyme replacement therapy, managing diabetes, and addressing complications. Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis:
• Individuals experiencing repeated episodes may require ongoing medical management and lifestyle modifications.
• Identifying and addressing underlying causes is essential for preventing recurrence.
Complications:
• Complications like pancreatic necrosis, pseudocysts, infection, or organ failure can prolong healing time.
• Treatment may involve drainage procedures, antibiotics, or surgical intervention. Recommendations:
• Follow healthcare provider's recommendations, adhere to treatment plans, and make lifestyle modifications.
• Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring may be necessary.
-Pancreatitis Diet Guidelines
• Clear liquid diet: Initially, a clear liquid diet may be recommended during the acute phase of pancreatitis.
• Low-fat diet: High-fat foods can stimulate the pancreas to release digestive enzymes, increasing inflammation and symptoms.
• Limit alcohol and caffeine: Alcohol and caffeinated beverages can irritate the pancreas and worsen inflammation.
• Complications like pancreatic necrosis, pseudocysts, infection, or organ failure can prolong healing time.
• Treatment may involve drainage procedures, antibiotics, or surgical intervention. Recommendations:
• Follow healthcare provider's recommendations, adhere to treatment plans, and make lifestyle modifications.
• Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring may be necessary.
Diet for Pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Diet Guidelines
• Clear liquid diet: Initially, a clear liquid diet may be recommended during the acute phase of pancreatitis.
• Low-fat diet: High-fat foods can stimulate the pancreas to release digestive enzymes, increasing inflammation and symptoms.
• Limit alcohol and caffeine: Alcohol and caffeinated beverages can irritate the pancreas and worsen inflammation.
• Small, frequent meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can reduce the workload on the pancreas and minimize digestive discomfort.
• High-fiber foods: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in the diet to provide fiber and essential nutrients.
• Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support digestion.
• Avoid trigger foods: Identify and avoid foods that worsen symptoms or trigger pancreatitis flare-ups.
• Enzyme supplements: In cases of pancreatic insufficiency, enzyme supplements may be recommended.
• Gradual reintroduction of foods: After the acute phase of pancreatitis has resolved, gradually reintroduce solid foods into the diet.
• Individualized approach: Work with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a personalized diet plan tailored to your specific needs.
Adherence to your healthcare provider's recommendations and a prescribed diet plan is crucial for effective pancreatitis management. Regular communication with your healthcare team allows for monitoring progress, addressing concerns, and necessary adjustments.
-Pancreatitis Consultation Aspects Not Often Emphasized
• Long-term dietary management: Doctors may not always emphasize the importance of long-term dietary management in managing chronic pancreatitis.
Key points include: • Low-fat diet, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
• Risk of complications: Not always discussed, but less common but potentially serious complications like pancreatic necrosis, infection, organ failure, or pancreatic cancer.
• Psychosocial impact: Pancreatitis can have significant emotional and social impacts, necessitating appropriate support and resources.
• Importance of lifestyle modifications: Doctors may not always provide specific guidance or resources for implementing lifestyle changes.
• Role of support groups and resources: Doctors may not always inform patients about the availability of these resources. Overall, open communication and proactive patient engagement can help address overlooked aspects and ensure effective management of the condition.
Medical Evaluation and Diagnosis:
• Pancreatitis is diagnosed based on medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. • Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach
. Acute Phase Management:
• Treatment focuses on resting the pancreas, rehydration, pain management, and antiemetics. • Hospitalization may be necessary for close monitoring and intensive care. Identifying and Addressing Underlying Causes: •
Gallstones may require gallbladder removal.
• Alcohol cessation is necessary for alcohol-induced pancreatitis.
• Medication review should be conducted to identify and discontinue contributing medications. Pain Management:
• Analgesics and non-pharmacological approaches may be prescribed for pain control. Nutritional Support
: • A clear liquid or low-fat diet may be recommended during acute episodes. • Enzyme replacement therapy may be prescribed for chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic insufficiency. Complication Management: • Pancreatic pseudocysts may require drainage procedures.
• Infections may be treated with antibiotics.
• Diabetes management may require insulin therapy or oral antidiabetic medications. Lifestyle Modifications: • Avoid alcohol and quit smoking.
• Maintain a healthy diet. Regular Follow-up and Monitoring:
• Regular appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress and address any complications. Prevention of Recurrence:
• Adopt healthy lifestyle habits.
• Adhere to prescribed medications.
• Attend regular check-ups and screenings. Patient Education and Support:
• Provide comprehensive education about pancreatitis.
• Offer support and resources. Conventional treatment for Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis Treatment Overview Medical Management during Acute Episodes:
• Fasting: Refraining from oral intake for a period to allow the pancreas to rest and inflammation to subside.
• Intravenous fluids: Fluid replacement therapy to prevent dehydration and maintain electrolyte balance.
• Pain management: Analgesic medications like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, or opioids to alleviate abdominal pain.
• Antiemetics: Medications to control nausea and vomiting. Identifying and Treating Underlying Causes:
• Gallstone removal: Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) may be necessary.
• Alcohol cessation: Patients with alcohol-induced pancreatitis are advised to abstain from alcohol.
• Medication review: Review and discontinuation of certain antibiotics, immunosuppressants, or diuretics. Nutritional Support:
• Diet modification: Initial clear liquid or low-fat diet recommended, gradually transitioning to solid foods as tolerated.
• Enzyme replacement therapy: Patients with chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic insufficiency may require pancreatic enzyme supplements. Complication Management:
• Pseudocyst drainage: Large or symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts may require drainage procedures.
• Infection treatment: Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections associated with pancreatitis.
• Diabetes management: Insulin therapy or oral antidiabetic medications may be required. Lifestyle Modifications:
• Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking to reduce the risk of pancreatic complications.
• Alcohol avoidance: Avoiding alcohol consumption to prevent further damage to the pancreas and reduce the risk of recurrence.
• Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
• Routine follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress, assess treatment efficacy, and address any complications. Prevention of Recurrence:
• Lifestyle modifications: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, ensuring medication adherence, and regular medical care.
• High-fiber foods: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in the diet to provide fiber and essential nutrients.
• Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support digestion.
• Avoid trigger foods: Identify and avoid foods that worsen symptoms or trigger pancreatitis flare-ups.
• Enzyme supplements: In cases of pancreatic insufficiency, enzyme supplements may be recommended.
• Gradual reintroduction of foods: After the acute phase of pancreatitis has resolved, gradually reintroduce solid foods into the diet.
• Individualized approach: Work with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a personalized diet plan tailored to your specific needs.
NOTE:
Adherence to your healthcare provider's recommendations and a prescribed diet plan is crucial for effective pancreatitis management. Regular communication with your healthcare team allows for monitoring progress, addressing concerns, and necessary adjustments.
What doctors won't tell you about Pancreatitis?
-Pancreatitis Consultation Aspects Not Often Emphasized
• Long-term dietary management: Doctors may not always emphasize the importance of long-term dietary management in managing chronic pancreatitis.
Key points include: • Low-fat diet, avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
• Risk of complications: Not always discussed, but less common but potentially serious complications like pancreatic necrosis, infection, organ failure, or pancreatic cancer.
• Psychosocial impact: Pancreatitis can have significant emotional and social impacts, necessitating appropriate support and resources.
• Importance of lifestyle modifications: Doctors may not always provide specific guidance or resources for implementing lifestyle changes.
• Role of support groups and resources: Doctors may not always inform patients about the availability of these resources. Overall, open communication and proactive patient engagement can help address overlooked aspects and ensure effective management of the condition.
Pancreatitis Treatment guide:
Medical Evaluation and Diagnosis:
• Pancreatitis is diagnosed based on medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. • Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach
. Acute Phase Management:
• Treatment focuses on resting the pancreas, rehydration, pain management, and antiemetics. • Hospitalization may be necessary for close monitoring and intensive care. Identifying and Addressing Underlying Causes: •
Gallstones may require gallbladder removal.
• Alcohol cessation is necessary for alcohol-induced pancreatitis.
• Medication review should be conducted to identify and discontinue contributing medications. Pain Management:
• Analgesics and non-pharmacological approaches may be prescribed for pain control. Nutritional Support
: • A clear liquid or low-fat diet may be recommended during acute episodes. • Enzyme replacement therapy may be prescribed for chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic insufficiency. Complication Management: • Pancreatic pseudocysts may require drainage procedures.
• Infections may be treated with antibiotics.
• Diabetes management may require insulin therapy or oral antidiabetic medications. Lifestyle Modifications: • Avoid alcohol and quit smoking.
• Maintain a healthy diet. Regular Follow-up and Monitoring:
• Regular appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress and address any complications. Prevention of Recurrence:
• Adopt healthy lifestyle habits.
• Adhere to prescribed medications.
• Attend regular check-ups and screenings. Patient Education and Support:
• Provide comprehensive education about pancreatitis.
• Offer support and resources. Conventional treatment for Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis Treatment Overview Medical Management during Acute Episodes:
• Fasting: Refraining from oral intake for a period to allow the pancreas to rest and inflammation to subside.
• Intravenous fluids: Fluid replacement therapy to prevent dehydration and maintain electrolyte balance.
• Pain management: Analgesic medications like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, or opioids to alleviate abdominal pain.
• Antiemetics: Medications to control nausea and vomiting. Identifying and Treating Underlying Causes:
• Gallstone removal: Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) may be necessary.
• Alcohol cessation: Patients with alcohol-induced pancreatitis are advised to abstain from alcohol.
• Medication review: Review and discontinuation of certain antibiotics, immunosuppressants, or diuretics. Nutritional Support:
• Diet modification: Initial clear liquid or low-fat diet recommended, gradually transitioning to solid foods as tolerated.
• Enzyme replacement therapy: Patients with chronic pancreatitis or pancreatic insufficiency may require pancreatic enzyme supplements. Complication Management:
• Pseudocyst drainage: Large or symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts may require drainage procedures.
• Infection treatment: Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections associated with pancreatitis.
• Diabetes management: Insulin therapy or oral antidiabetic medications may be required. Lifestyle Modifications:
• Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking to reduce the risk of pancreatic complications.
• Alcohol avoidance: Avoiding alcohol consumption to prevent further damage to the pancreas and reduce the risk of recurrence.
• Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
• Routine follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor progress, assess treatment efficacy, and address any complications. Prevention of Recurrence:
• Lifestyle modifications: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, ensuring medication adherence, and regular medical care.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

vajan or motapa ko kam karne ke liye kya tip hai
१) मोटापा से छुटकारा पाने के उपयोगी टिप्स क्या है?
आज के भागदौड़ वाले ज़िंदगी में मोटापा बड़ी समस्याओं बन गयी है। भारत में भी इसका तरह की बीमारी अब बढ़ती जा रही है. यह केवल दिखावे की बात नहीं अब नहीं है, बल्कि गंभीर समस्याओं भी बन सकता है।
- मोटापे का सीधा संबंध मधुमेह, हाई ब्लड प्रेशर, और जोड़ों के दर्द जैसी कई तरह की बीमारी में से है।
- शरीर में जब भी ज़्यादा चर्बी जमा होने के कारण से यह स्थिति होती है। और धीरे-धीरे यह जीवनशैली को असर करने लगती है।
- मोटापा ऐसी समस्या नहीं है, जिसे की नियंत्रित न किया जा सके। कुछ घरेलू उपाय और जीवनशैली से जुड़े बदलाव अपनाकर इसे कम किया जा सकता है।
- मोटापा को कम करने का पहला और जरूरी कदम है , की आहार पर नियंत्रण रखना है। असंतुलित और ज्यादा कैलोरी वाला भोजनकरने से वजन बढ़ाने का सबसे बड़ा कारण होता है।
- जंक फूड, और ज्यादातर तैलीय खाना खाने से और मीठे पेय पदार्थ से भी मोटापा तेजी से बढ़ाते हैं।
-जिसके स्थान पर संतुलित और पौष्टिक वाला आहार लेना चाहिए। भोजन में ताज़ा फल, और हरी सब्ज़ियाँ, और दालें शामिल करना बेहतर रहता है। यह पाचन को भी सही रखता है और शरीर को जरुरी पोषण भी देता है।
- खाने का समय और इसका तरीका भी मोटापे को कण्ट्रोल करने में अहम भूमिका निभाता है। छोटे-छोटे अंतराल पर हल्का भोजन करना होता है। जिस से की पाचन तंत्र पर दबाव नहीं पड़ता है। और शरीर को ज़रूरी ऊर्जा मिलती रहती है।
- एक बार में अधिक खाना खाने से बचना चाहिए। और धीरे-धीरे खाना खाने की आदत रखे। क्योंकि कम भोजन में ही पेट भरा हुआ होता है।
- शारीरिक गतिविधि भी मोटापा को कम करने का सबसे असरकारक तरीका है।
- आजकल के जीवनशैली में लोग घंटों तक लगातार बैठे रहते हैं, जिस से की शरीर की अतिरिक्त कैलोरी भी खर्च नहीं हो पाती है। - डेली कम से कम आधा घंटा तक तेज़ चलना, या दौड़ना, कसरत करना जरूरी है।
- थोड़ी दूरी पर पैदल चलने जाना और नियमित रूप से स्ट्रेचिंग करना जिस से की कैलोरी बर्न करने में भी मदद करता है।
- दिनभर में सही मात्रा में पानी पीने से भी शरीर हाइड्रेट रहता है, और भूख लगने की समस्या भी कम होती है। कई बार तो,प्यास को लोग तो, भूख भी समझ लेते हैं और अनावश्यक भोजन करते हैं। इसलिए पानी पीने की आदत को मजबूत बनाना चाहिए।
- फाइबर से भरपूर मिलने वाला आहार जैसे की, फल, हरी सब्ज़ियाँ और सलाद मोटापा को कम करने में मदद करते हैं। फाइबर पेट को लंबे समय तक भरा रखता है और ज्यादा खाने से रोकता है।
- तनाव और सही से नींद भी नहीं मिलना मोटापे का बड़ा कारण है। तनाव के समय में तो कुछ ऐसे हार्मोन बनते हैं, जिस से की, खाने की इच्छा और भी बढ़ जाती हैं और लोग ज्यादा खाना खाने लगते हैं।
- अपने समय पर सोने की आदत डालने से मोटापा कम करने में भी आसानी होती है।
- टीवी को देखते हुए या मोबाइल चलने में ज्यादा खाने की आदत से बचना चाहिए। और ध्यान लगाकर के भोजन करना चाहिए।
- यात्रा के दौरान बाहर का हेल्दी स्नैक्स रखना भी फायदेमंद होता है। जब अचानक भूख लगने लग जाये तो, तैलीय नाश्ते की बजाय हमेशा फल, मुरमुरा, या तो भूना चना को खाएँ।
- अचानक से बहुत ज्यादा डाइटिंग करना या बिना सोचे-समझे खाना को छोड़ देना शरीर के लिए हानि हो सकता है।
- धीरे-धीरे वजन को कम करने की कोशिश करें और रोज़ाना छोटे-छोटे परिवतन करें। यह बदलाव लंबे समय तक टिके रहते हैं और शरीर को स्वस्थ रखते हैं।

latex allergy treatment in homeopathy | latex allergy kya hai
१) लेटेक्स एलर्जी : बचाव और देखभाल के उपयोगी टिप्स क्या है?
आज के तेज़ रफ्तारभरी ज़िंदगी में हम डेली कुछ चीज़ों का इस्तेमाल करते हैं जिन में की **लेटेक्स** होता है। - लेटेक्स एक तरह का प्राकृतिक रबर है, जो रबर के पेड़ में से निकाले गए रस से बनता है।
- इसका उपयोग दस्ताने बनाने में , गुब्बारे, रबर बैंड और टायर, जूते, और खिलौनों तक में इसका उपयोग होता है।
- कुछ लोगों के लिए लेटेक्स *एलर्जन* भी बन सकता है.
२) लेटेक्स एलर्जी क्या है?
यह एलर्जी एक प्रतिरक्षा तंत्र की प्रतिक्रिया है। जब संवेदनशील व्यक्ति का शरीर लेटेक्स के संपर्क में आ जाने से आता है, उसकी रोग प्रतिरोधक प्रणाली इसे खतरे के रूप में पहचान लेती है और एलर्जिक लक्षण पैदा करती है।
३) लेटेक्स एलर्जी के क्या लक्षण है?
- *त्वचा के संबंधी जैसे लक्षण** : – खुजली का होना , लाल रंग के चकत्ते, सूजन। - *श्वसन संबंधी के लक्षण: – छींक का आना, नाक का बहना, गले में खराश जैसा होना और सांस लेने में परेशानी का होना। *गंभीर लक्षण*: – ब्लड प्रेशर अचानक से कम हो जाना , सांस रुकने जैसी समस्या, बेहोशी जैसा लगना
३) किन लोगों में लेटेक्स एलर्जी का खतरा सबसे ज़्यादा होता है?
- 1.*हेल्थकेयर वर्कर* :– डॉ, लैब टेक्नीशियन, जो बार-बार लेटेक्स दस्ताने का उपयोग करते हैं।
- 2.*सर्जरी से निकले मरीज* :– जिनके कई बार सर्जरी हुआ है, उनमें लेटेक्स एलर्जी की संभावना और भी बढ़ जाती है। - 3. *रबर उद्योग में काम करने वाले लोग.*
4. *एलर्जी और अस्थमा के दर्दी * – जिन के रोग प्रतिरोधक प्रणाली पहले से संवेदनशील होती है।
४) लेटेक्स एलर्जी से बचाव के उपयोगी टिप्स क्या है?
#1. लेटेक्स से दूरी बनाएँ रखे. - लेटेक्स दस्तानों की जगह पर **नाइट्राइल दस्ताने** का उपयोग करें।
- गुब्बारे, रबर वाले बैंड और लेटेक्स कवर करने वाले किताबें, खिलौनों से दूर रहे। २) यदि आप को लेटेक्स एलर्जी हो ,तो **डॉ. और नर्स को पहले ही बता दें** जिस से की लेटेक्स-फ्री टूल का उपयोग करें। - अस्पतालों में **लेटेक्स-फ्री किट्स** ही अब उपलब्ध होती हैं।
३) डॉ. के अनुसार एलर्जी की दवा को हमेशा ही साथ में रखें। ४) घर और कार्यस्थल पर सावधानी
* घर में बच्चों के लिए **लेटेक्स-फ्री विकल्प** को चुनें।
* ऑफिस में या फैक्ट्री में लेटेक्स से जुड़े हुए प्रोडक्ट का कम से कम उपयोग करें।
* यदि परिवार में किसी को भी एलर्जी है, तो उन्हें एक्सपोज़र से बचाएँ। ५).यदि आप को केले खाने, या कीवी, और पपीता, शकरकंद और टमाटर से एलर्जी हो, तो उन से खाने से दूर रहे. क्योंकि एलर्जी को ट्रिगर कर सकते हैं। ६). एलर्जी होने के शुरुआती लक्षण दिखाई देने पर अपने डॉ. से संपर्क करें।
* स्किन टेस्ट या खून टेस्ट के माध्यम से लेटेक्स एलर्जी का पता कर सकते है.
४) लेटेक्स एलर्जी वाले लोगों की देखभाल?
*बच्चों में लेटेक्स एलर्जी है, तो माता-पिता को स्कूल और उनके टीचर को एलर्जी के बारे में बात करे। *हॉस्पिटल में लेटेक्स-फ्री सर्जिकल किट का उपयोग करें।
* किचन के सफाई के लिए लेटेक्स-फ्री विकल्प को ही अपनाएँ।

kawasaki rog se bachne ke liye kya tip hai
१) कावासाकी रोग से बचाव और देखभाल के टिप्स?
यह रोग बच्चों में होने वाली बहुत ही दुर्लभ और गंभीर समस्या है। शरीर की रक्त वाहिकाओं में सूजन आ जाती है ,और यदि समय पर ध्यान न दिया जाए तो यह दिल की धमनियों को हानि भी पहुँचा सकता है।
- यह रोग खासक ५ साल से कम उम्र के बच्चों को असर करता है। इसका सही तरह से पूरा कारण अभी तक नहीं पता है, इसलिए रोकथाम और देखभाल पर ध्यान देना बहुत ज़रूरी है।
* यदि छोटे बच्चों में लगातार ५ दिन से भी अधिक समय तक तेज बुखार रहे, तो इसे सामान्य नही समझें और तुरंत ही डॉ.से सलाह ले।
- अपने बच्चों के होंठ या जीभ, और आँखें और हाथ-पाँव की स्थिति पर डेली रूप से ध्यान देना सही होता है.
* स्वच्छ वातावरण बनाएँ
बच्चों को हमेशा से ही साफ कपड़े को पहनाएँ, और उनका कमरा को डेली साफ़ करना सही होता है.
- बच्चों के खिलौनों और उनके मुँह में डेल गए खिलौनों को नियमित रूप से साफ करें।
* बच्चों के रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता को मजबूत करने के लिए संतुलित आहार देना बेहद ही आवश्यक है। उन्हें ताजे फल, हरी सब्ज़ियाँ, दूध और दालें दें।
*
-अपने बच्चों को पुरे दिनभर में उचित पानी को पिलाएँ। और उसके साथ में ही नारियल का पानी, और ताजे फलों का जूस को पिलाना भी लाभकारी होता है।
* बच्चों को थकाने वाले खेल-कूद से दूर रखें। उन्हें सही आराम ,नींद का सही समय सुनिश्चित करें।
-
सही नींद से बच्चों के शरीर की रिकवरी बहुत ही तेज़ होती है. और रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता भी बढ़ती है। *यदि बच्चे को पहले कावासाकी रोग से प्रभावित हो चुका है, तो डॉ. की सलाह के अनुसार समय-समय पर स्वास्थ्य की जाँच ज़रूर करवाएँ। खासतौर पर हृदय की जाँच कराना ज़रूरी है ,जिस से की दिल की धमनियों पर किसी भी तरह का असर है,तो समय रहते पता चल सके। * बच्चों को खुश और तनाव मुक्त में रखें। जिस से की कोई भी तरह का असर उनके शरीर पर नहीं हो सकता है।
२) कावासाकी रोग के घरेलू देखभाल क्या है?
- अपने बच्चे का ध्यान देना बहुत ही ज़रूरी है। जिस से की हल्का और पौष्टिक भोजन दें, और साफ कपड़े को ही पहनाएँ।
- डॉ. के द्वारा दी गई दवाइ को समय पर ही दें और डॉ. से पूछे बिना दवा को बंद न करें।
- बच्चों को छोटे-छोटे व्यायाम की आदत डालें , जिस से की , रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता बढ़ाने पर ध्यान दें. -बच्चों को हमेशा से ही उबला हुआ पानी को ही पिलाएँ।और बाहर का खुला हुआ खाना बिल्कुल नही दें। यह संक्रमण का खतरा बढ़ाता है।
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
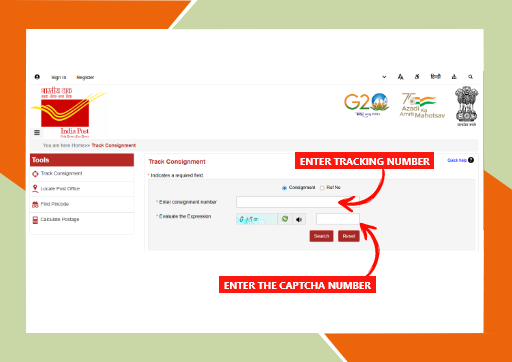
brahm homeopathy medicine tracking details
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी मेडिसिन ट्रैकिंग कैसे करें?
अगर आपने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से दवा ऑर्डर की है और आप उसकी डिलीवरी की स्थिति जानना चाहते हैं, तो आप आसानी से इंडिया पोस्ट की वेबसाइट पर जाकर अपनी दवा को ट्रैक कर सकते हैं।
- ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी अधिकतर दवाएं भारत सरकार की इंडिया पोस्ट सेवा के माध्यम से भेजता है, जिसमें हर पार्सल का एक यूनिक ट्रैकिंग नंबर होता है।
Brahm Homeopathy Medicine Tracking Details.
- ट्रैकिंग के लिए सबसे पहले India Post की वेबसाइट पर जाएं। वहां “Track Consignment” विकल्प पर क्लिक करें। इसके बाद स्क्रीन पर दिख रही जगह पर अपना ट्रैकिंग नंबर डालें जो आपको ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से SMS या Email के माध्यम से मिला होगा। - फिर स्क्रीन पर दिखाई दे रही कैप्चा कोड को सही-सही भरें और “Search” बटन पर क्लिक करें।
- इसके बाद आपको आपकी दवा का पूरा स्टेटस दिखेगा – जैसे कि पार्सल कहां पहुंचा है, कब डिलीवर होगा आदि। यह प्रक्रिया सरल है और घर बैठे आप अपने ऑर्डर की जानकारी आसानी से प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
इस प्रकार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की ट्रैकिंग सुविधा पारदर्शिता और भरोसेमंद सेवा का परिचायक है।
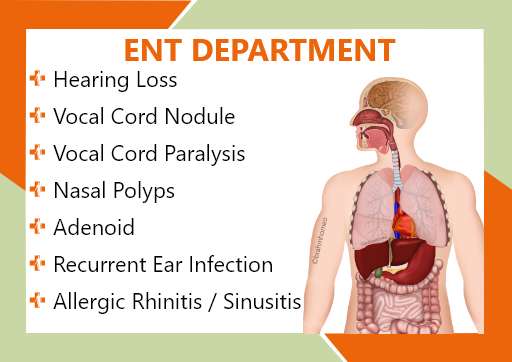
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
Diseases
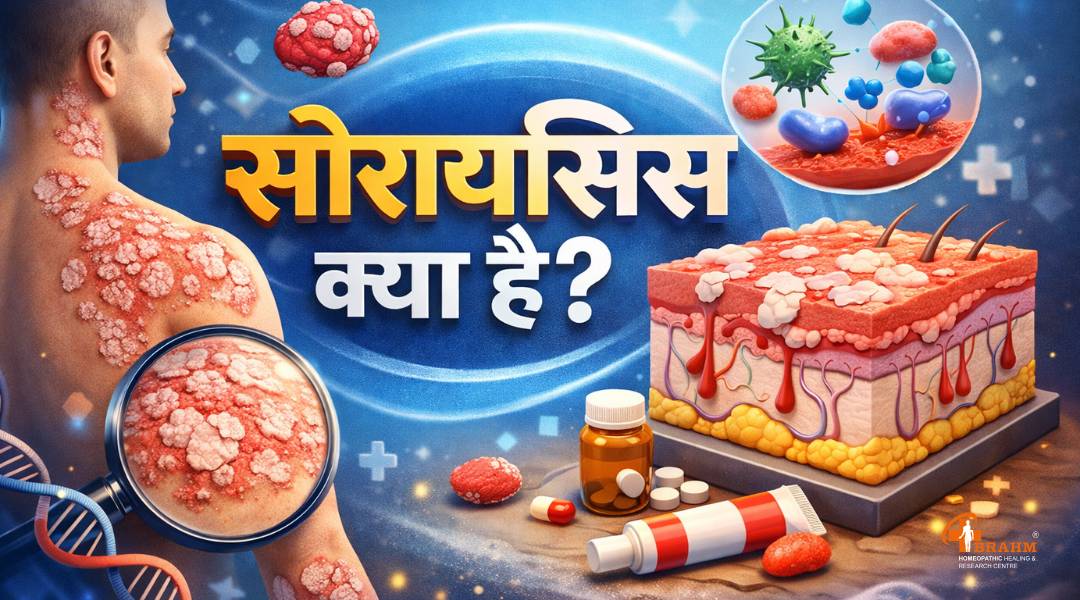
psoriasis kaise hota hai or kyu failta hai?
सोरायसिस क्या है?
सोरायसिस एक दीर्घकालिक (Chronic) त्वचा रोग है, जो मुख्य रूप से शरीर की त्वचा को प्रभावित करता है। यह कोई संक्रामक बीमारी नहीं है, यानी यह छूने, साथ रहने या कपड़े साझा करने से नहीं फैलती। इस रोग में त्वचा की कोशिकाएँ सामान्य से बहुत तेज़ी से बनने लगती हैं, जिससे त्वचा पर लाल, सूखे और मोटे चकत्ते बन जाते हैं जिन पर सफेद या चांदी जैसी पपड़ी जम जाती है।
सोरायसिस केवल त्वचा तक सीमित नहीं रहता, बल्कि कुछ मामलों में यह नाखूनों, सिर की त्वचा (स्कैल्प) और यहाँ तक कि जोड़ों (Psoriatic Arthritis) को भी प्रभावित कर सकता है। यह बीमारी किसी भी उम्र में हो सकती है, लेकिन अधिकतर यह युवावस्था या मध्यम आयु में दिखाई देती है।
सोरायसिस कैसे होता है?
सोरायसिस मुख्य रूप से इम्यून सिस्टम (प्रतिरक्षा तंत्र) की गड़बड़ी के कारण होता है। सामान्य अवस्था में त्वचा की नई कोशिकाएँ बनने में लगभग 28–30 दिन का समय लेती हैं। लेकिन सोरायसिस में यह प्रक्रिया केवल 3–5 दिनों में पूरी हो जाती है।
जब नई कोशिकाएँ इतनी तेज़ी से बनती हैं, तो पुरानी कोशिकाओं को झड़ने का समय नहीं मिल पाता। परिणामस्वरूप ये कोशिकाएँ त्वचा की सतह पर जमा होने लगती हैं और मोटी, पपड़ीदार त्वचा का रूप ले लेती हैं।
इस पूरी प्रक्रिया में शरीर का इम्यून सिस्टम गलती से स्वस्थ त्वचा कोशिकाओं पर हमला करने लगता है, जिससे सूजन और लालिमा बढ़ जाती है।
सोरायसिस होने के कारण?
सोरायसिस का कोई एक निश्चित कारण नहीं है, लेकिन कुछ मुख्य कारण और जोखिम कारक माने जाते हैं: 1. आनुवंशिक कारण यदि परिवार में किसी को सोरायसिस है, तो अगली पीढ़ी में इसके होने की संभावना बढ़ जाती है। हालांकि, यह जरूरी नहीं कि हर मामले में यह विरासत में ही मिले।
2. इम्यून सिस्टम की गड़बड़ी
यह एक ऑटोइम्यून रोग है, जिसमें शरीर की प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली त्वचा की स्वस्थ कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुँचाने लगती है। 3. तनाव अधिक मानसिक तनाव सोरायसिस को शुरू कर सकता है या पहले से मौजूद बीमारी को और गंभीर बना सकता है। 4. संक्रमण गले का संक्रमण (Strep Throat) या अन्य बैक्टीरियल/वायरल संक्रमण सोरायसिस को ट्रिगर कर सकते हैं, खासकर बच्चों और युवाओं में।
5. त्वचा पर चोट
कट लगना, जलना, खरोंच या सर्जरी के निशान पर सोरायसिस के चकत्ते उभर सकते हैं, जिसे Koebner Phenomenon कहा जाता है। 6. कुछ दवाइयाँ
कुछ दवाइयाँ जैसे—बीटा ब्लॉकर्स, लिथियम, या मलेरिया की दवाइयाँ—सोरायसिस को बढ़ा सकती हैं। 7. जीवनशैली से जुड़े कारण • धूम्रपान • अधिक शराब का सेवन • मोटापा ये सभी सोरायसिस के जोखिम को बढ़ा सकते हैं।
सोरायसिस के लक्षण?
सोरायसिस के लक्षण व्यक्ति-व्यक्ति में अलग हो सकते हैं। इसके सामान्य लक्षण निम्नलिखित हैं: 1. त्वचा पर लाल चकत्ते
त्वचा पर लाल रंग के उभरे हुए पैच दिखाई देते हैं, जिन पर सफेद या चांदी जैसी पपड़ी होती है। 2. खुजली और जलन
प्रभावित जगह पर तेज़ खुजली, जलन या दर्द हो सकता है। 3. त्वचा का सूखना और फटना
त्वचा बहुत ज़्यादा सूखी हो जाती है और कभी-कभी उसमें से खून भी निकल सकता है। 4. स्कैल्प सोरायसिस सिर की त्वचा पर रूसी जैसी मोटी पपड़ी जम जाती है, जो कंधों तक गिर सकती है। 5. नाखूनों में बदलाव • नाखूनों पर गड्ढे पड़ना • नाखूनों का मोटा या पीला होना• नाखून का त्वचा से अलग होना
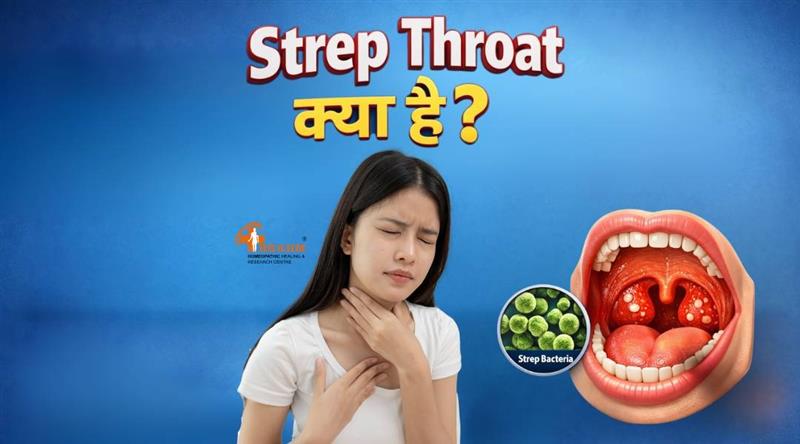
Strep Throat kya hai or kaise hota hai?
Strep Throat क्या है?
Strep Throat (स्ट्रेप थ्रोट) गले का एक बैक्टीरियल संक्रमण है, जो Streptococcus pyogenes नामक बैक्टीरिया के कारण होता है। इसे Group A Streptococcus (GAS) भी कहा जाता है। यह संक्रमण मुख्य रूप से गले, टॉन्सिल (tonsils) और आसपास के ऊतकों को प्रभावित करता है।
स्ट्रेप थ्रोट सामान्य गले की खराश से अलग होता है। सामान्य गले में दर्द अक्सर वायरल संक्रमण (जैसे सर्दी-जुकाम) के कारण होता है, जबकि स्ट्रेप थ्रोट बैक्टीरिया के कारण होता है और इसमें लक्षण अधिक गंभीर हो सकते हैं।
यह बीमारी बच्चों और किशोरों में अधिक आम है, लेकिन वयस्कों को भी हो सकती है। अगर इसका सही समय पर इलाज न किया जाए, तो यह गंभीर जटिलताओं का कारण बन सकता है, जैसे रूमेटिक फीवर या किडनी की बीमारी।
Strep Throat कैसे होता है?
स्ट्रेप थ्रोट संक्रमित व्यक्ति से स्वस्थ व्यक्ति में आसानी से फैलता है। यह मुख्य रूप से सांस के माध्यम से फैलता है।
संक्रमण फैलने के तरीके:
1 . खांसने और छींकने से • जब संक्रमित व्यक्ति खांसता या छींकता है, तो बैक्टीरिया हवा में फैल जाते हैं और दूसरा व्यक्ति उन्हें सांस के साथ अंदर ले सकता है।
2 . सीधे संपर्क से • संक्रमित व्यक्ति के संपर्क में आने से, जैसे हाथ मिलाना, गले लगना, या उनके इस्तेमाल किए हुए रूमाल/तौलिये को छूना। 3 . दूषित वस्तुओं से (Fomites) • बैक्टीरिया दरवाजे के हैंडल, पानी की बोतल, चम्मच, कप या खिलौनों पर रह सकते हैं। इन्हें छूकर फिर मुँह या नाक छूने से संक्रमण हो सकता है।
4 . भीड़भाड़ वाली जगहों में ज्यादा खतरा • स्कूल, हॉस्टल, डेकेयर सेंटर और ऑफिस जैसी जगहों पर संक्रमण तेजी से फैल सकता है।
Strep Throat के कारण?
स्ट्रेप थ्रोट का मुख्य कारण Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Strep) बैक्टीरिया है। हालांकि, कुछ परिस्थितियाँ संक्रमण का खतरा बढ़ा देती हैं।
मुख्य कारण: • Group A Streptococcus बैक्टीरिया से संक्रमण • संक्रमित व्यक्ति के संपर्क में आना
जोखिम बढ़ाने वाले कारक:
• कमजोर प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली (Low Immunity) • बार-बार सर्दी-जुकाम होना • बच्चों का स्कूल या डेकेयर जाना • भीड़भाड़ वाले स्थानों में रहना • सर्दी के मौसम में अधिक संक्रमण • पहले से गले या टॉन्सिल की समस्या होना
यह ध्यान रखना जरूरी है कि हर गले का दर्द स्ट्रेप थ्रोट नहीं होता। अधिकतर गले के संक्रमण वायरस के कारण होते हैं, लेकिन स्ट्रेप थ्रोट बैक्टीरिया के कारण होता है।
Strep Throat के लक्षण?
स्ट्रेप थ्रोट के लक्षण आमतौर पर अचानक शुरू होते हैं और वायरल गले के संक्रमण से अधिक तीव्र होते हैं। #प्रारंभिक लक्षण
• गले में तेज दर्द
• निगलने में कठिनाई • गले में खरोंच जैसा महसूस होना • अचानक बुखार आना #मुख्य लक्षण • तेज बुखार (38.3°C या उससे अधिक)
• लाल और सूजे हुए टॉन्सिल • टॉन्सिल पर सफेद धब्बे या पस (white patches)
• गर्दन की गांठों (लिम्फ नोड्स) में सूजन और दर्द • सिरदर्द
• शरीर में दर्द
• थकान और कमजोरी #बच्चों में दिखने वाले लक्षण • उल्टी या पेट दर्द • चिड़चिड़ापन • खाने-पीने में कमी
Strep Throat का निदान?
डॉक्टर आमतौर पर दो तरह की जांच करते हैं: 1 . Rapid Strep Test – कुछ मिनटों में रिजल्ट मिलता है। 2 . Throat Culture (गले का स्वैब टेस्ट) – अधिक सटीक, लेकिन रिजल्ट आने में 24–48 घंटे लग सकते हैं।
Strep Throat का इलाज? चूंकि यह बैक्टीरियल संक्रमण है, इसलिए इसका इलाज एंटीबायोटिक्स से किया जाता है। #एंटीबायोटिक्स लेने से: • लक्षण जल्दी ठीक होते हैं. • संक्रमण फैलने का खतरा कम होता है. • गंभीर जटिलताओं का जोखिम घटता है. दवाइयाँ हमेशा पूरे कोर्स तक लेनी चाहिए, भले ही लक्षण जल्दी ठीक हो जाएँ। निष्कर्ष Strep Throat एक सामान्य लेकिन गंभीर बैक्टीरियल संक्रमण है, जो समय पर इलाज न मिलने पर जटिलताएँ पैदा कर सकता है। इसके लक्षण सामान्य गले के दर्द से अलग होते हैं और इसमें तेज बुखार, गले में बहुत दर्द और टॉन्सिल पर सफेद धब्बे दिख सकते हैं।

urticaria kya hai or kaise failta hai ?
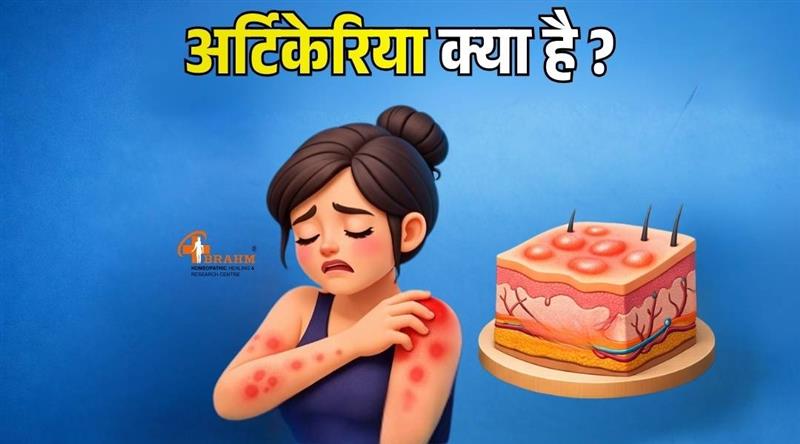
अर्टिकेरिया क्या है?
अर्टिकेरिया, जिसे आम भाषा में पित्ती या हाइव्स (Hives) कहा जाता है, एक प्रकार की त्वचा से संबंधित एलर्जिक समस्या है। इसमें त्वचा पर अचानक लाल या गुलाबी रंग के उभरे हुए चकत्ते, सूजन और तेज खुजली होने लगती है। ये चकत्ते शरीर के किसी भी हिस्से में हो सकते हैं जैसे—चेहरा, हाथ, पैर, पीठ या पेट।
अर्टिकेरिया कोई संक्रामक बीमारी नहीं है, यानी यह एक व्यक्ति से दूसरे व्यक्ति में नहीं फैलती। यह समस्या कुछ घंटों से लेकर कई हफ्तों या महीनों तक भी रह सकती है।
अर्टिकेरिया कैसे होता है?
अर्टिकेरिया तब होता है जब शरीर की प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली (Immune System) किसी बाहरी या आंतरिक तत्व को गलत तरीके से खतरा समझ लेती है। इसके कारण शरीर में मौजूद मास्ट सेल्स (Mast Cells) से हिस्टामिन (Histamine) नामक रसायन निकलता है।
हिस्टामिन निकलने से: • त्वचा की रक्त वाहिकाएं फैल जाती हैं • त्वचा में सूजन आ जाती है • खुजली और जलन होने लगती है
यही प्रक्रिया पित्ती के चकत्तों का कारण बनती है।
अर्टिकेरिया के प्रकार?
अर्टिकेरिया को मुख्य रूप से दो प्रकारों में बांटा जाता है:
1. तीव्र अर्टिकेरिया
• 6 हफ्तों से कम समय तक रहता है • अक्सर एलर्जी के कारण होता है
• दवाओं, भोजन या संक्रमण से जुड़ा होता है
2. दीर्घकालिक अर्टिकेरिया
• बार-बार ठीक होकर फिर उभर आता है • कई बार कारण स्पष्ट नहीं होता
अर्टिकेरिया होने के कारण?
अर्टिकेरिया के कई कारण हो सकते हैं, जिनमें से कुछ प्रमुख हैं: 1. खाद्य पदार्थ
• अंडा
• मूंगफली • समुद्री भोजन • दूध
• चॉकलेट
• फूड कलर और प्रिज़रवेटिव्स 2 . संक्रमण • वायरल इंफेक्शन • बैक्टीरियल इंफेक्शन • सर्दी-जुकाम या बुखार
3 . मौसम और वातावरण• अधिक ठंड या गर्मी
• पसीना • धूप • ठंडी हवा या पानी 4 . तनाव (Stress)
मानसिक तनाव और चिंता भी अर्टिकेरिया को बढ़ा सकते हैं। 5 . कीड़े-मकोड़ों का काटना
मच्छर, मधुमक्खी या अन्य कीड़ों के काटने से भी पित्ती हो सकती है। 6 . ऑटोइम्यून कारण
कई बार शरीर की प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली खुद के ऊतकों पर हमला करने लगती है, जिससे क्रॉनिक अर्टिकेरिया होता है।
अर्टिकेरिया के लक्षण?
अर्टिकेरिया के लक्षण व्यक्ति के अनुसार अलग-अलग हो सकते हैं, लेकिन सामान्य लक्षण इस प्रकार हैं: • त्वचा पर लाल या गुलाबी रंग के उभरे चकत्ते • तेज खुजली
• चकत्तों का आकार बदलते रहना • चकत्तों का कुछ घंटों में गायब होकर फिर उभरना • त्वचा में जलन या चुभन
• चेहरे, होंठ, आंखों या गले में सूजन (Angioedema)
#गंभीर स्थिति में: • सांस लेने में दिक्कत • गले में सूजन • चक्कर आना अर्टिकेरिया की पहचान? अर्टिकेरिया की पहचान मुख्य रूप से: • मरीज के लक्षणों • मेडिकल हिस्ट्री • एलर्जी टेस्ट • ब्लड टेस्ट के आधार पर की जाती है। कई बार क्रॉनिक अर्टिकेरिया में कारण पता नहीं चल पाता।
निष्कर्ष
अर्टिकेरिया एक आम लेकिन परेशान करने वाली त्वचा समस्या है। सही समय पर पहचान और उचित इलाज से इसे नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है। यदि पित्ती बार-बार हो रही है या लंबे समय तक बनी रहती है, तो त्वचा रोग विशेषज्ञ से परामर्श लेना अत्यंत आवश्यक है। सही जीवनशैली और सावधानी से इस बीमारी को काफी हद तक नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है।
Videos

kya pancreatitis normal ho sakta hai?
१)पैंक्रियाटाइटिस क्या है? क्या यह सामान्य हो सकता है?
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक गंभीर स्वास्थ्य समस्या है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में सूजन आ जाती है। अग्न्याशय पेट के पीछे स्थित एक महत्वपूर्ण अंग है जो हमारे शरीर में पाचन एंजाइम और इंसुलिन जैसे हार्मोन बनाने का काम करता है।
जब किसी कारण से पाचन एंजाइम समय से पहले ही सक्रिय हो जाते हैं, तो वे भोजन को पचाने के बजाय अग्न्याशय के ऊतकों को ही नुकसान पहुंचाने लगते हैं। इस स्थिति को ही पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
२)क्या पैंक्रियाटाइटिस अपने आप ठीक हो सकता है?
यह इस बात पर निर्भर करता है कि बीमारी कितनी गंभीर है।
कुछ मामलों में हल्का पैंक्रियाटाइटिस सही इलाज, आराम और डॉक्टर की निगरानी से पूरी तरह ठीक हो सकता है। लेकिन यदि बीमारी गंभीर हो जाए तो अस्पताल में भर्ती होकर इलाज करवाना आवश्यक हो सकता है।
#1. तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस(Acute Pancreatitis)
- यह अचानक शुरू होने वाली स्थिति होती है। - कई बार यह कुछ दिनों के इलाज से ठीक भी हो सकता है।
- समय पर इलाज मिलने से मरीज पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हो सकता है।
#2. दीर्घकालिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस(Chronic Pancreatitis)
- यह लंबे समय तक रहने वाली समस्या होती है। - इसमें अग्न्याशय धीरे-धीरे कमजोर और क्षतिग्रस्त होने लगता है।
- यदि समय पर उपचार न किया जाए तो स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है।
३) क्या पैंक्रियाटाइटिस सामान्य बीमारी है?
अगर बात तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस की करें तो कई मामलों में सही इलाज और आराम से सामान्य स्थिति में आ सकता है। - अस्पताल में मरीज को कुछ दिनों तक दवाइयाँ, तरल पदार्थ और हल्का भोजन दिया जाता है, जिससे उसकी स्थिति में सुधार होता है। लेकिन इसे बिल्कुल साधारण बीमारी समझना भी सही नहीं है क्योंकि।
- यह अचानक गंभीर रूप ले सकता है. - किडनी और फेफड़ों जैसे महत्वपूर्ण अंगों पर असर पड़ सकता है. इसीलिए पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को कभी भी हल्के में नहीं लेना चाहिए।
४) पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने के प्रमुख कारण?
यह बीमारी कई कारणों से हो सकती है, जैसे: की, - पित्ताशय की पथरी (Gallstones), अत्यधिक शराब का सेवन, खून में ट्राइग्लिसराइड का अधिक स्तर, कुछ दवाओं के साइड इफेक्ट, पारिवारिक कारण
५) पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण?
इस बीमारी में कई प्रकार के लक्षण दिखाई दे सकते हैं, जैसे: की, - पेट के ऊपरी हिस्से में तेज दर्द , दर्द का पीठ तक फैलना, मतली और उल्टी, पेट में सूजन या भारीपन, भूख कम लगना - अगर किसी व्यक्ति को बहुत तेज दर्द या लगातार उल्टी हो रही हो तो उसे तुरंत डॉक्टर के पास ले जाना चाहिए।
५) पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज और रिकवरी?
- इलाज मरीज की स्थिति के अनुसार किया जाता है। सामान्यत:
- कुछ समय तक ठोस भोजन बंद किया जाता है. - शरीर में तरल की कमी पूरी करने के लिए IV फ्लूड दिया जाता है.
#कारण के अनुसार उपचार#
यदि बीमारी का कारण पित्त की पथरी या कोई अन्य समस्या है, तो उसका भी इलाज किया जाता है। आमतौर पर हल्के मामलों में मरीज 3 से 7 दिनों में ठीक हो सकता है।लेकिन यदि सूजन बहुत अधिक हो जाए, ऊतक नष्ट होने लगें या संक्रमण फैल जाए तो ICU में इलाज की आवश्यकता पड़ सकती है।
६) क्या पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पूरी तरह ठीक हो सकता है?
तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कई मामलों में सही इलाज और समय पर देखभाल से मरीज पूरी तरह ठीक हो सकता है। लेकिन दीर्घकालिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस में बीमारी को नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है, पूरी तरह समाप्त करना हमेशा संभव नहीं होता।
७) पैंक्रियाटाइटिस से बचाव कैसे करें?
इस बीमारी से बचने के लिए कुछ महत्वपूर्ण सावधानियाँ अपनानी चाहिए: - शराब का सेवन पूरी तरह बंद करें।
- कम वसा (Low Fat) वाला संतुलित आहार लें.erte

omega 3 sharir mein kya fayda karta hai
१) ओमेगा-3 शरीर में क्या फायदा करता है?
ओमेगा-3 जरुरी फैटी एसिड है, जो के हमारे शरीर के लिए बहुत ही जरुरी होता है। इसे आवश्यक कहा जाता है, क्योंकि हमारा शरीर इसको नहीं बना सकता है, इसलिए हम इसको भोजन के माध्यम से लेना होता है.
- ओमेगा-3 हृदय, मस्तिष्क, आंखों, त्वचा तथा संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य के लिए बेहद लाभकारी माना जाता है।
२) ओमेगा-3 मुख्य रूप से तीन प्रकार का होता है?
- अल्फा-लिनोलेनिक एसिड :: यह मुख्य रूप से पौधों से प्राप्त होता है। - इकोसापेंटेनोइक एसिड :: यह वसायुक्त मछलियों में होता है। डोकोसाहेक्सेनोइक एसिड :: यह मस्तिष्क, आंखों के लिए है।
वसायुक्त मछलियां जैसे की, Salmon, Sardine तथा Mackerel ओमेगा-3 के अच्छे स्रोत हैं। 1. हृदय को स्वस्थ रखता है.
ओमेगा-3 का बड़ा लाभ हृदय का स्वास्थ्य होता है. - अच्छे कोलेस्ट्रॉल को बढ़ाता है. - ट्राइग्लिसराइड स्तर को कण्ट्रोल करता है. नियमित रूप से ओमेगा-3 लेने पर हार्ट अटैक तथा स्ट्रोक का खतरा कम हो सकता है।
2. मस्तिष्क की शक्ति को बढ़ाता है। - DHA मस्तिष्क का जरुरी घटक है। ओमेगा-3:
- याददाश्त को अच्छा करता है. - एकाग्रता को भी बढ़ाता है. बच्चों में यह मस्तिष्क के विकास के लिए आवश्यक है. # 3. जोड़ों तथा हड्डियों के लिए फायदेमंद - किसी को गठिया ,जोड़ों में दर्द के समस्या है, तो ओमेगा-3 लाभकारी हो सकता है। - जोड़ों के अकड़न को कम करता है.
- चलने-फिरने में भी आसानी होता है.
# 4. आंखों के लिए भी जरूरी होता है.
- DHA आंखों के रेटिना का जरुरी भाग है। ओमेगा-3
- आंखों का सूखापन कम करता है.
- उम्र बढ़ने के साथ में होने वाली दृष्टि के समस्याओं का जोखिम को कम करता है.
आजकल स्क्रीन का उपयोग करने वाले लोगों के लिए ओमेगा-3 का सेवन महत्वपूर्ण हो गया है।
5. गर्भावस्था तथा बच्चों के लिए लाभकारी - गर्भावस्था के दौरान ओमेगा-3 मां तथा बच्चो दोनों के लिए जरूरी होता है। - शिशु के मस्तिष्क तथा आंखों के विकास में मदद करता है. - बच्चों के सीखने की क्षमता को अच्छा बनाता है # 6. त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए फायदेमंद - ओमेगा-3 त्वचा को चमकदार बनाने में भी मदद करता है। - त्वचा के नमी को भी बनाए रखता है. - मुंहासों , सूजन को भी कम करता है. - बालों के मजबूती में सहायक होता है 7. वजन को नियंत्रण तथा मधुमेह में मददगार - ओमेगा-3 मेटाबॉलिज्म को अच्छा बनाता है, तथा शरीर के चर्बी को कम करने में मदद कर सकता है।
- यह इंसुलिन को बढ़ाने में मदद करता है, जिस से मधुमेह को कण्ट्रोल में सहायता हो सकती है। ३) ओमेगा-3 के दैनिक आवश्यकता क्या है?
- वयस्कों के लिए दिन में २५०-५०० मिलीग्राम EPA , DHA पर्याप्त माना जाता है। पर सही मात्रा व्यक्ति के उम्र, स्वास्थ्य के स्थिति , डॉक्टर की सलाह पर निर्भर है।
#ओमेगा-3 में से क्या - क्या स्रोत है?
#मांसाहारी स्रोत में# - सैल्मन मछली - सार्डिन - फिश का ऑयल #शाकाहारी स्रोत में# - अखरोट , सोयाबीन का तेल भोजन से सही मात्रा में न मिले, तो डॉ. के सलाह से सप्लीमेंट को दिया जा सकता है।
४) ओमेगा-3 के दुष्प्रभाव होते हैं क्या ? ज्यादा मात्रा में लेने से,
- पेट भी खराब हो सकता है.
- गैस या तो,एसिडिटी हो सकती है।
- खून भी पतला होने का खतरा बढ़ सकता है.

Vitamin E sharir ke liye kyu jaruri hai?
१) विटामिन E शरीर के लिए क्यों जरूरी है?
- विटामिन E शक्तिशाली एंटीऑक्सीडेंट विटामिन है, जो हमारे शरीर के लिए बहुत ही जरुरी है। यह मुख्य रूप से सेल्स के सुरक्षा, प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत , त्वचा तथा बालों के स्वास्थ्य के लिए जाना जाता है। - विटामिन E शरीर में वसा के साथ मिलकर के कार्य करता है, तथा कोशिकाओं के झिल्लियों को क्षति से भी बचाता है।
२) विटामिन E क्या है?
विटामिन E समूह है जिसे टोकॉफेरॉल भी कहा जाता है। इस में अल्फा-टोकॉफेरॉल सबसे एक्टिव तथा शरीर के लिए सबसे उपयोगी है।
यह विटामिन प्राकृतिक रूप से कई तरह के खाद्य पदार्थों में मिलता है,जैसे कि,
- हरी पत्तेदार वाले सब्जियाँ।
- बीज तथा नट्स। - साबुत अनाज।
* कुछ फल में जैसे कि, एवोकाडो तथा किवी।
३) शरीर में विटामिन E का क्या रोल होता है?
विटामिन E कई तरह से शरीर को लाभ पहुंचाता है।, जैसे की, a) एंटीऑक्सीडेंट का काम - विटामिन E फ्री रेडिकल्स रासायनिक पदार्थ हैं जो के शरीर की कोशिकाओं को क्षति पहुँचा सकते हैं , तथा उम्र बढ़ने, कैंसर, हृदय रोग जैसी समस्याओं का कारण बन सकते हैं।
- विटामिन E इन से लड़कर के कोशिकाओं के सुरक्षा करता है। b) हृदय स्वास्थ्य में सहायक - विटामिन E रक्त वाहिका में कोलेस्ट्रॉल के ऑक्सीकरण प्रक्रिया को रोकता है। - यह विशेष रूप से खराब कोलेस्ट्रॉल के ऑक्सीकरण को कम करके धमनियों में ब्लॉकेजकी संभावना घटाता है। c) प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को भी मजबूत बनाता है. - इम्यून सिस्टम को भी मजबूत बनाता है।
- यह सफेद रक्त कोशिकाओं के कार्य को बढ़ाता है, तथा शरीर को संक्रमणों से लड़ने में सक्षम बनाता है। d) त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक - त्वचा की नमी को बनाए रखने, झुर्रियों को कम करने तथा सूरज की UV किरणों से सुरक्षा में मदद करता है। e) मांसपेशियों तथा तंत्रिकाओं के स्वास्थ्य के लिए - विटामिन E मांसपेशियों तथा नसों में ऑक्सीजन को पहुंचाने, सूजन को कम करने में भी मदद करता है।
४)विटामिन E के कमी होने का लक्षण?
शरीर में विटामिन E की कमी हो जाए, तो इसके मुख्य लक्षण हैं, - मांसपेशियों में कमजोरी तथा थकान जैसा लगना
- दृष्टि के समस्याएँ।
- हाथ-पैर में झुनझुनी या सुन्नपन जैसा लगना- त्वचा तथा बालों के समस्याएँ
५) विटामिन E का अधिक सेवन तथा सावधानियाँ?
विटामिन E की कमी से बचना भी जरुरी है, पर इसका ज्यादा सेवन भी हानिकारक हो सकता है।
- रक्त का पतला हो सकता है.
- रक्तस्राव का जोखिम भी बढ़ सकता है. विटामिन E का सेवन संतुलित मात्रा में तथा डॉ. की सलाह से करना चाहिए। ६) विटामिन E को प्राकृतिक रूप से प्राप्त करना
- नट्स तथा बीजों को नाश्ते में उपयोग करें।
- हरी पत्तेदार सब्जि को सलाद के रूप में लें। - मूंगफली तेल का उपयोग कम करे । - किवी , आम जैसे फलों को डाइट में उपयोग करे.
