
ankylosing spondylitis
What food is good for ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory illness that is classified as arthritis. Although the data is limited, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet that includes whole grains and calcium-rich foods may help some people with their symptoms.
What is the recovery time for ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory illness that is classified as arthritis. Although the data is limited, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet that includes whole grains and calcium-rich foods may help some people with their symptoms.
What is the last stage of spondylitis?
Some patients with early AS develop more severe illness. The bones of the spine can fuse together, a condition known as "ankylosis." Doctors refer to this advanced phase as the "bamboo spine." You may have severe back pain, stiffness, and discomfort, limiting your flexibility and movement.

What is the age limit for ankylosing spondylitis?
The condition often begins between the ages of 20 and 40, however it can begin before the age of 10. It affects men more than women. Ankylosing spondylitis is a condition that causes intermittent pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips.
Should I be worried about ankylosing spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a complicated disorder that can affect several regions of your body. It can complicate your daily life and lead to more serious health problems.
Stories

chronic pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियास ठीक करने के उपाय
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस एक बीमारी है जो आपके पैंक्रियास में हो सकती है। पैंक्रियास आपके पेट में एक लंबी ग्रंथि है जो भोजन को पचाने में आपकी मदद करती है। यह आपके रक्त प्रवाह में हार्मोन भी जारी करता है जो आपके शरीर को ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग करने में मदद करता है। यदि आपका पैंक्रियास क्षतिग्रस्त हो गया है, तो पाचन एंजाइम सामान्य रूप से आपकी छोटी आंत में नहीं जा सकते हैं और आपका शरीर ऊर्जा के लिए भोजन का उपयोग नहीं कर सकता है।
पैंक्रियास शरीर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है जो हार्मोन इंसुलिन का उत्पादन करके रक्त शर्करा को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। यदि इस अंग को नुकसान होता है, तो इससे मानव शरीर में गंभीर समस्याएं हो सकती हैं। ऐसी ही एक समस्या है जब पैंक्रियास में सूजन हो जाती है, जिसे तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस कहा जाता है।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस पैंक्रियास की सूजन है जो लंबे समय तक रह सकती है। इससे पैंक्रियास और अन्य जटिलताओं को स्थायी नुकसान हो सकता है। इस सूजन से निशान ऊतक विकसित हो सकते हैं, जो इंसुलिन उत्पन्न करने वाली कोशिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा सकते हैं। यह पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ वाले लगभग 45 प्रतिशत लोगों में मधुमेह का कारण बन सकता है। भारी शराब का सेवन भी वयस्कों में पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकता है। ऑटोइम्यून और आनुवंशिक रोग, जैसे सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस, कुछ लोगों में पुरानी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बन सकते हैं।
उत्तर भारत में, ऐसे बहुत से लोग हैं जिनके पास पीने के लिए बहुत अधिक है और कभी-कभी एक छोटा सा पत्थर उनके पित्ताशय में फंस सकता है और उनके अग्न्याशय के उद्घाटन को अवरुद्ध कर सकता है। इससे उन्हें अपना खाना पचाने में मुश्किल हो सकती है। 3 हाल ही में एशिया-प्रशांत क्षेत्र के विभिन्न देशों में किए गए एक सर्वेक्षण के अनुसार दक्षिण भारत में पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ की व्यापकता प्रति 100,000 जनसंख्या पर 114-200 मामले हैं।
Chronic Pancreatitis Patient Cured Report
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण ?
-कुछ लोगों को पेट में दर्द होता है जो पीठ तक फैल सकता है। -यह दर्द मतली और उल्टी जैसी चीजों के कारण हो सकता है। -खाने के बाद दर्द और बढ़ सकता है। -कभी-कभी किसी के पेट को छूने पर दर्द महसूस हो सकता है। -व्यक्ति को बुखार और ठंड लगना भी हो सकता है। वे बहुत कमजोर और थका हुआ भी महसूस कर सकते हैं।
क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण ?
-पित्ताशय की पथरी -शराब
-रक्त में उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड का स्तर -रक्त में उच्च कैल्शियम का स्तर
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है?
होम्योपैथी में क्रोनिक पैंक्रियाटाइटिस नेक्रोसिस का उपचार उपचारात्मक है। आप कितने समय तक इस बीमारी से पीड़ित रहेंगे यह काफी हद तक आपकी उपचार योजना पर निर्भर करता है। ब्रह्म अनुसंधान पर आधारित चिकित्सकीय रूप से सिद्ध वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी के इलाज में अत्यधिक प्रभावी हैं। हमारे पास आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करने, सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों, रोग के पाठ्यक्रम का दस्तावेजीकरण करने, रोग के चरण, पूर्वानुमान और जटिलताओं को समझने की क्षमता है, हमारे पास अत्यधिक योग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है। फिर वे आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताएंगे, आपको एक उचित आहार योजना (क्या खाएं और क्या नहीं खाएं), व्यायाम योजना, जीवनशैली योजना और कई अन्य कारक प्रदान करेंगे जो आपके समग्र स्वास्थ्य में सुधार कर सकते हैं। पढ़ाना। व्यवस्थित उपचार रोग ठीक होने तक होम्योपैथिक औषधियों से उपचार करें। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, चाहे वह थोड़े समय के लिए हो या कई सालों से। हम सभी ठीक हो सकते हैं, लेकिन बीमारी के प्रारंभिक चरण में हम तेजी से ठीक हो जाते हैं। पुरानी या देर से आने वाली या लंबे समय तक चलने वाली बीमारियों को ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगता है। समझदार लोग इस बीमारी के लक्षण दिखते ही इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं। इसलिए, यदि आपको कोई असामान्यता नज़र आती है, तो कृपया तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।

Acute Necrotizing pancreas treatment in hindi
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ ?
आक्रामक अंतःशिरा द्रव पुनर्जीवन, दर्द प्रबंधन, और आंत्र भोजन की जल्द से जल्द संभव शुरुआत उपचार के मुख्य घटक हैं। जबकि उपरोक्त सावधानियों से बाँझ परिगलन में सुधार हो सकता है, संक्रमित परिगलन के लिए अतिरिक्त उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लक्षण ? - बुखार - फूला हुआ पेट - मतली और दस्त तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के कारण ?
- अग्न्याशय में चोट - उच्च रक्त कैल्शियम स्तर और रक्त वसा सांद्रता
ऐसी स्थितियाँ जो अग्न्याशय को प्रभावित करती हैं और आपके परिवार में चलती रहती हैं, उनमें सिस्टिक फाइब्रोसिस और अन्य आनुवंशिक विकार शामिल हैं जिनके परिणामस्वरूप बार-बार अग्नाशयशोथ होता है|
क्या एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रिएटाइटिस का इलाज होम्योपैथी से संभव है ?
हां, होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनकर एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का इलाज संभव है। होम्योपैथिक उपचार चुनने से आपको इन दवाओं का कोई साइड इफेक्ट नहीं होगा और यह समस्या को जड़ से खत्म कर देता है, इसीलिए आपको अपने एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के इलाज के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार का ही चयन करना चाहिए।
आप तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ से कैसे छुटकारा पा सकते हैं ?
शुरुआती चरण में सर्वोत्तम उपचार चुनने से आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस से छुटकारा मिल जाएगा। होम्योपैथिक उपचार का चयन करके, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे विश्वसनीय उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करता है। एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार सबसे अच्छा इलाज है। जैसे ही आप एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक करने के लिए अपना उपचार शुरू करेंगे, आपको निश्चित परिणाम मिलेंगे।
होम्योपैथिक उपचार से तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ का इलाज संभव है। आप कितने समय से बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, इसका उपचार योजना पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। इससे कोई फर्क नहीं पड़ता कि आप कब से अपनी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं, या तो हाल ही में या कई वर्षों से - हमारे पास सब कुछ ठीक है, लेकिन बीमारी के शुरुआती चरण में, आप तेजी से ठीक हो जाएंगे। पुरानी स्थितियों के लिए या बाद के चरण में या कई वर्षों की पीड़ा के मामले में, इसे ठीक होने में अधिक समय लगेगा। बुद्धिमान व्यक्ति हमेशा इस बीमारी के किसी भी लक्षण को देखते ही तुरंत इलाज शुरू कर देते हैं, इसलिए जैसे ही आपमें कोई असामान्यता दिखे तो तुरंत हमसे संपर्क करें।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एवं रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
ब्रह्म अनुसंधान आधारित, चिकित्सकीय रूप से प्रमाणित, वैज्ञानिक उपचार मॉड्यूल इस बीमारी को ठीक करने में बहुत प्रभावी है। हमारे पास सुयोग्य डॉक्टरों की एक टीम है जो आपके मामले का व्यवस्थित रूप से निरीक्षण और विश्लेषण करती है, रोग की प्रगति के साथ-साथ सभी संकेतों और लक्षणों को रिकॉर्ड करती है, इसकी प्रगति के चरणों, पूर्वानुमान और इसकी जटिलताओं को समझती है। उसके बाद वे आपको आपकी बीमारी के बारे में विस्तार से बताते हैं, आपको उचित आहार चार्ट [क्या खाएं या क्या न खाएं], व्यायाम योजना, जीवन शैली योजना प्रदान करते हैं और कई अन्य कारकों के बारे में मार्गदर्शन करते हैं जो व्यवस्थित प्रबंधन के साथ आपकी सामान्य स्वास्थ्य स्थिति में सुधार कर सकते हैं। जब तक यह ठीक न हो जाए तब तक होम्योपैथिक दवाओं से अपनी बीमारी का इलाज करें।
तीव्र नेक्रोटाइज़िंग अग्नाशयशोथ के लिए आहार ?
कुपोषण और पोषण संबंधी कमियों को रोकने के लिए, सामान्य रक्त शर्करा के स्तर को बनाए रखने और मधुमेह, गुर्दे की समस्याओं और पुरानी अग्नाशयशोथ से जुड़ी अन्य स्थितियों को रोकने या बेहतर ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए, अग्नाशयशोथ की तीव्र घटना से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है।
यदि आप एक स्वस्थ आहार योजना की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। हमारे विशेषज्ञ आपकी व्यक्तिगत आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप एक योजना बनाने में आपकी सहायता कर सकते हैं

Pancreatitis treatment in hindi
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस ?
जब पैंक्रियाटाइटिसमें सूजन और संक्रमण हो जाता है तो इससे पैंक्रिअटिटिस नामक रोग हो जाता है। पैंक्रियास एक लंबा, चपटा अंग है जो पेट के पीछे पेट के शीर्ष पर छिपा होता है। पैंक्रिअटिटिस उत्तेजनाओं और हार्मोन का उत्पादन करके पाचन में मदद करता है जो आपके शरीर में ग्लूकोज के प्रसंस्करण को विनियमित करने में मदद करते हैं।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लक्षण:
-पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होना। -बेकार वजन घटाना. -पेट का ख़राब होना.
-शरीर का असामान्य रूप से उच्च तापमान। -पेट को छूने पर दर्द होना। -तेज़ दिल की धड़कन. -हाइपरटोनिक निर्जलीकरण.
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के कारण:
-पित्ताशय में पथरी. -भारी शराब का सेवन.
-भारी खुराक वाली दवाएँ। -हार्मोन का असंतुलन. -रक्त में वसा जो ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स का कारण बनता है। -आनुवंशिकता की स्थितियाँ. -पेट में सूजन ।
क्या होम्योपैथी पैंक्रियाटाइटिस को ठीक कर सकती है?
हाँ, होम्योपैथीपैंक्रियाटाइटिसको ठीक कर सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपको पैंक्रिअटिटिस के लिए सबसे भरोसेमंद उपचार देना सुनिश्चित करती है।
पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा उपचार क्या है?
यदि पैंक्रियाज अच्छी तरह से काम नहीं कर रहा है तो होम्योपैथिक उपचार वास्तव में बेहतर होने में मदद करने का एक अच्छा तरीका है। जब आप उपचार शुरू करते हैं, तो आप जल्दी परिणाम देखेंगे। बहुत सारे लोग इस इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जा रहे हैं और वे वास्तव में अच्छा कर रहे हैं। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी आपके पैंक्रियाज के को बेहतर बनाने में मदद करने के लिए आपको सबसे तेज़ और सुरक्षित तरीका प्रदान करना सुनिश्चित करती है।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक हीलिंग एंड रिसर्च सेंटर की उपचार योजना
बीमार होने पर लोगों को बेहतर महसूस कराने में मदद करने के लिए हमारे पास एक विशेष तरीका है। हमारे पास वास्तव में स्मार्ट डॉक्टर हैं जो ध्यान से देखते हैं और नोट करते हैं कि बीमारी व्यक्ति को कैसे प्रभावित कर रही है। फिर, वे सलाह देते हैं कि क्या खाना चाहिए, व्यायाम करना चाहिए और स्वस्थ जीवन कैसे जीना चाहिए। वे व्यक्ति को ठीक होने में मदद करने के लिए विशेष दवा भी देते हैं। यह तरीका कारगर साबित हुआ है!
Tips

dehydration treatment in homeopathy
1. Dehydration treatment
When the body loses more fluid than it takes in, it causes an imbalance in electrolytes and fluids needed for normal body function. This can be due to excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, or not drinking enough water.
While severe dehydration requires medical attention, mild to moderate dehydration can often be treated effectively at home without the use of drugs or medication. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can help restore hydration and balance in a safe and gentle way.
1. Replenish water
The most important step in treating dehydration is to drink water. Clean water is the best way to rehydrate the body. Drink water slowly and in small sips rather than drinking large amounts at once, especially if nausea occurs. -Drinking small amounts at regular intervals allows the body to absorb fluids more effectively.
2. Consume natural electrolytes
When we sweat due to illness, we also lose essential electrolytes like sodium, potassium and magnesium. Without these, just drinking water is not enough. You can make an electrolyte drink at home by mixing the following:
- 1 liter of clean water - 6 teaspoons of sugar
- 1/2 teaspoon of salt This solution helps a lot in balancing electrolytes and can be more effective than plain water.
- Coconut water is a natural alternative as it has a good balance of sodium, potassium and other electrolytes.
3. Eat hydrating foods
Some foods are high in water and can help restore hydration naturally. For example,
watermelon, cucumber, oranges, lettuce - Some foods in your diet can provide both fluids and essential nutrients.
4. Avoid dehydrating substances
- Coffee, energy drinks
- Alcohol
- Salty snacks
These can worsen fluid loss. Sticking to water and natural fluids is the best option until hydration is restored.
5. Rest
If the dehydration is caused by heat or strenuous physical activity, resting in a cool, shady area is a must. - Avoiding excessive sweating or exertion helps the body recover more easily. - Using a fan, cool cloth or taking a warm bath also helps regulate body temperature
6. Monitor symptoms
It is important to monitor your condition. Signs of dehydration include: - Increased urine with a light color
- Decreased thirst
If symptoms persist or worsen - such as dizziness, very dark urine, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Final Thoughts
Dehydration can often be treated effectively without medication or drugs, especially when it's caught early.
-While natural remedies are helpful, it's important to see a doctor if symptoms become severe or don't respond to home remedies

hamare sarir ke liye sabji ke labh
सब्जियाँ हमारे आहार का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा हैं। इनमें कई प्रकार के विटामिन, खनिज, एंटीऑक्सीडेंट और फाइबर होते हैं, जो शरीर को स्वस्थ बनाए रखते हैं। सब्जियों का सेवन न केवल रोगों से बचाव करता है बल्कि संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य को भी बनाए रखता है।
सब्जियों के प्रकार और उनके लाभ
1. हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ (Leafy Green Vegetables)
हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ पोषण से भरपूर होती हैं और शरीर को कई तरह के आवश्यक तत्व प्रदान करती हैं।
-1. पालक (Spinach) लाभ: आयरन, कैल्शियम और फाइबर से भरपूर। हड्डियों और मांसपेशियों को मजबूत बनाता है। एनीमिया और कब्ज से बचाव करता है।
2. सरसों के पत्ते (Mustard Greens)
-लाभ: -हड्डियों के लिए फायदेमंद। -इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है। -त्वचा और बालों को स्वस्थ रखता है।
3. मेथी (Fenugreek Leaves)
-लाभ: -डायबिटीज को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करता है। -पाचन को सुधारता है और भूख बढ़ाता है।
4. धनिया और पुदीना (Coriander & Mint Leaves)
-लाभ: -पाचन को सुधारते हैं। -विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालते हैं। -त्वचा को चमकदार बनाते हैं।
2. जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ (Root Vegetables)
जड़ वाली सब्जियाँ फाइबर और आवश्यक खनिजों से भरपूर होती हैं।
5. गाजर (Carrot)

sarir ke liye vitamin or unke labh
हमारे शरीर के लिए सभी विटामिन और उनके लाभ
विटामिन हमारे शरीर के लिए आवश्यक पोषक तत्व हैं, जो शरीर के विभिन्न कार्यों को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में मदद करते हैं। ये सूक्ष्म पोषक तत्व होते हैं, लेकिन शरीर में इनकी भूमिका बहुत महत्वपूर्ण होती है। विटामिन की कमी से कई स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं, इसलिए संतुलित आहार लेना जरूरी है।
विटामिन कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
-विटामिन दो प्रकार के होते हैं: -1. वसा में घुलनशील विटामिन (Fat-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में वसा में संग्रहित होते हैं और जरूरत पड़ने पर उपयोग किए जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन A, D, E और K आते हैं।
-2. जल में घुलनशील विटामिन (Water-Soluble Vitamins): ये विटामिन शरीर में जमा नहीं होते और मूत्र के माध्यम से बाहर निकल जाते हैं। इनमें विटामिन C और सभी B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन आते हैं।
विटामिन और उनके लाभ
1. विटामिन A (रेटिनॉल, बीटा-कैरोटीन)
भूमिका:
आँखों की रोशनी को बनाए रखता है।
त्वचा और इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है।
हड्डियों और दांतों के विकास में सहायक है।
स्रोत:
गाजर पालकआम, शकरकंद, डेयरी उत्पाद, अंडे, मछली का तेल।
कमी के प्रभाव:
रतौंधी (नाइट ब्लाइंडनेस)
त्वचा में रूखापन
रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी
---
2. विटामिन B-कॉम्प्लेक्स (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12)
B-कॉम्प्लेक्स विटामिन ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र और रक्त निर्माण में मदद करते हैं। B1 (थायमिन)
भूमिका: ऊर्जा उत्पादन, तंत्रिका तंत्र के कार्यों में सहायक।
स्रोत: साबुत अनाज, बीन्स, सूरजमुखी के बीज, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: कमजोरी, भूख न लगना, तंत्रिका तंत्र की समस्या।
B2 (राइबोफ्लेविन)
भूमिका: त्वचा, आँखों और ऊर्जा उत्पादन के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: दूध, दही, अंडे, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: होंठों में दरारें, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B3 (नियासिन)
भूमिका: कोलेस्ट्रॉल को नियंत्रित करता है और पाचन में सहायक होता है।
स्रोत: मूंगफली, मशरूम, टमाटर, चिकन, मछली।
कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा रोग, मानसिक कमजोरी। B5 (पैंटोथेनिक एसिड)
भूमिका: हार्मोन उत्पादन और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: मशरूम, एवोकाडो, दूध, ब्रोकली।
कमी के प्रभाव: थकान, सिरदर्द।
B6 (पाइरिडोक्सिन)
भूमिका: तंत्रिका तंत्र और प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली को मजबूत करता है।
स्रोत: केला, चिकन, सोयाबीन, आलू।
कमी के प्रभाव: अवसाद, त्वचा रोग।
B7 (बायोटिन)
भूमिका: बालों और त्वचा के स्वास्थ्य को बनाए रखता है।
स्रोत: अंडे, मूंगफली, फूलगोभी।
कमी के प्रभाव: बाल झड़ना, त्वचा की समस्याएँ। B9 (फोलिक एसिड)
भूमिका: डीएनए निर्माण और गर्भावस्था में जरूरी।
स्रोत: दालें, हरी सब्जियाँ, बीन्स। कमी के प्रभाव: एनीमिया, जन्म दोष।
B12 (कोबालामिन)
भूमिका: लाल रक्त कोशिकाओं और तंत्रिका तंत्र के लिए आवश्यक।
स्रोत: मांस, अंडे, डेयरी उत्पाद। कमी के प्रभाव: स्मरण शक्ति की कमजोरी, एनीमिया।
---
3. विटामिन C (एस्कॉर्बिक एसिड)
भूमिका: इम्यून सिस्टम को मजबूत करता है, त्वचा को चमकदार बनाता है, और घाव भरने में मदद करता है। स्रोत: संतरा, नींबू, स्ट्रॉबेरी, टमाटर, हरी मिर्च।
कमी के प्रभाव: स्कर्वी, मसूड़ों से खून आना, रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता में कमी।
---
4. विटामिन D (कोलेकल्सीफेरोल)
भूमिका: हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाता है और कैल्शियम के अवशोषण में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: सूर्य का प्रकाश, मछली, अंडे, दूध।
कमी के प्रभाव: हड्डियों में कमजोरी, रिकेट्स।
---
5. विटामिन E (टोकोफेरॉल)
भूमिका: एंटीऑक्सीडेंट के रूप में कार्य करता है और त्वचा तथा बालों के लिए लाभदायक है। स्रोत: बादाम, सूरजमुखी के बीज, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियाँ। कमी के प्रभाव: त्वचा की समस्याएँ, कमजोरी।
---
6. विटामिन K (फायलोक्विनोन)
भूमिका: रक्त को थक्का जमाने (ब्लड क्लॉटिंग) में मदद करता है।
स्रोत: पालक, ब्रोकोली, हरी सब्जियाँ।
कमी के प्रभाव: चोट लगने पर खून न रुकना। ---
निष्कर्ष
शरीर को सभी विटामिनों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि सभी अंग सही से काम कर सकें। इनके लिए संतुलित आहार लेना बहुत जरूरी है। यदि विटामिन की कमी हो, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेकर सप्लीमेंट्स भी लिए जा सकते हैं। लेकिन, प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से विटामिन प्राप्त करना हमेशा सबसे अच्छा होता है।
-आपके शरीर की जरूरतों के अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक सेंटर में भी विटामिन डेफिशिएंसी का होम्योपैथिक उपचार उपलब्ध है। यदि आपको कोई लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक से संपर्क करें और स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर बनाएँ।
Testimonials

body weakness treatment
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से 10 महीने में चमत्कारी इलाज: एक मरीज की कहानी
आज के समय में जब लोग तरह-तरह की बीमारियों से जूझ रहे हैं, तब होम्योपैथी चिकित्सा कई मरीजों के लिए आशा की किरण बन रही है। ऐसी ही एक प्रेरणादायक कहानी है एक मरीज की, जिसने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के माध्यम से 10 महीने में अपनी बीमारी से निजात पाई।
शुरुआत में थी थकान और शरीर में भारीपन
मरीज ने बताया, "मुझे कई दिनों से शरीर में थकान, भारीपन और बेचैनी महसूस हो रही थी। यह परेशानी धीरे-धीरे इतनी बढ़ गई कि रोजमर्रा के काम भी कठिन लगने लगे। मेरी माँ पहले से ही ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी क्लीनिक में इलाज करा रही थीं। उन्होंने बताया कि उन्हें वेरीकोज वेन्स की समस्या थी और यहाँ के इलाज से उन्हें बहुत लाभ हुआ था। उनकी सलाह पर मैं भी यहाँ आया।"
होम्योपैथी इलाज का असर मात्र एक सप्ताह में
मरीज के अनुसार, "जब मैंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा से परामर्श लिया और उनकी सलाह के अनुसार दवाएं लेना शुरू किया, तो सिर्फ एक हफ्ते के भीतर ही मुझे सुधार महसूस होने लगा। मेरी थकान कम हो गई, शरीर की ऊर्जा बढ़ने लगी और पहले की तुलना में मैं ज्यादा सक्रिय महसूस करने लगा।"
लगातार 10 महीने तक किया उपचार, मिली पूरी राहत
मरीज ने लगातार 10 महीने तक ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाएं लीं और सभी निर्देशों का पालन किया। उन्होंने कहा, "लगभग 15 दिनों के अंदर ही मेरी स्थिति में काफी सुधार हुआ और अब 10 महीने बाद मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ महसूस कर रहा हूँ। यह सब डॉक्टर प्रदीप कुशवाहा और ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी की दवाओं की वजह से संभव हुआ।"
होम्योपैथी: सभी बीमारियों के लिए वरदान
मरीज ने आगे कहा, "इस क्लिनिक का माहौल बहुत अच्छा है और इलाज का तरीका बेहद प्रभावी है। यहाँ की दवाएँ बहुत असरदार हैं और मुझे इनके इस्तेमाल से कोई साइड इफेक्ट भी नहीं हुआ। यह सच में होम्योपैथी का सबसे बेहतरीन केंद्र है। मैं सभी मरीजों से अनुरोध करूंगा कि अगर वे किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान हैं, तो एक बार ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी का इलाज जरूर लें। यह एक बीमार मरीजों के लिए किसी स्वर्ग से कम नहीं है।"
निष्कर्ष
इस मरीज की कहानी यह साबित करती है कि सही चिकित्सा और सही मार्गदर्शन से कोई भी बीमारी ठीक हो सकती है। ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी में न केवल आधुनिक चिकित्सा पद्धति का समावेश है, बल्कि यहाँ मरीजों की समस्याओं को गहराई से समझकर उनका संपूर्ण इलाज किया जाता है। यदि आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी एक बेहतरीन विकल्प हो सकता है।

acute pancreatitis ka ilaaj
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: एक मरीज की जीवन बदलने वाली कहानी
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस: एक गंभीर समस्या
एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें अग्न्याशय में तीव्र सूजन हो जाती है। जब यह समस्या उत्पन्न होती है, तो मरीज को शुरुआत में इसकी जानकारी नहीं होती, लेकिन दर्द इतना असहनीय होता है कि उसे तुरंत अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की आवश्यकता पड़ती है। इस स्थिति का मुख्य कारण अनुचित जीवनशैली, जंक फूड, शराब का सेवन, ऑटोइम्यून बीमारियां, कुछ रसायन और विकिरण हो सकते हैं। यदि समय रहते सही इलाज नहीं किया गया, तो यह स्थिति क्रॉनिक पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में बदल सकती है।
अमन बाजपेई की प्रेरणादायक यात्रा
मैं, अमन बाजपेई, पिछले 1.5 वर्षों से एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का मरीज था। यह समय मेरे लिए बेहद कठिन था। मैं बहुत परेशान था, खाना खाने तक के लिए तरस गया था। पिछले 7-8 महीनों में मैंने रोटी तक नहीं खाई, केवल खिचड़ी और फल खाकर गुजारा कर रहा था। बार-बार मुझे इस बीमारी के हमले झेलने पड़ रहे थे। हर 5-10 दिनों में दवा लेनी पड़ती थी, लेकिन कोई लाभ नहीं हो रहा था।
इस बीमारी के इलाज में मैंने 6-7 लाख रुपये खर्च कर दिए। दिल्ली और झांसी समेत कई बड़े अस्पतालों में इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई राहत नहीं मिली। मेरा वजन 95 किलो से घटकर 55 किलो हो गया और मैं बहुत कमजोर हो गया था। तभी मुझे सोशल मीडिया के माध्यम से ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के बारे में पता चला।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी: उम्मीद की एक नई किरण
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी वह जगह है जहां कम खर्च में उत्कृष्ट इलाज संभव है। मैंने आज तक किसी भी डॉक्टर या अस्पताल में इतना अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं देखा। डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा सर ने मुझे एक नई जिंदगी दी। पहले मुझे लगा था कि मैं शायद कभी ठीक नहीं हो पाऊंगा, लेकिन आज मैं पूरी तरह स्वस्थ हूं।
मैं सभी मरीजों को यही सलाह दूंगा कि वे पैसे की बर्बादी न करें और सही इलाज के लिए ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी जाएं। यह भारत में एक्यूट पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस के लिए सबसे अच्छा अस्पताल है। मेरे लिए डॉ. प्रदीप कुशवाहा किसी देवता से कम नहीं हैं।
वैज्ञानिक रूप से प्रमाणित उपचार पद्धति
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी के विशेषज्ञों ने शोध आधारित एक विशेष उपचार पद्धति विकसित की है, जिससे न केवल लक्षणों में सुधार होता है बल्कि बीमारी को जड़ से ठीक किया जाता है। हजारों मरीज इस उपचार का लाभ ले रहे हैं और उनकी मेडिकल रिपोर्ट में भी उल्लेखनीय सुधार देखा गया है।
यदि आप भी इस बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं और सही इलाज की तलाश कर रहे हैं, तो ब्रह्म होम्योपैथी से संपर्क करें। यह न केवल बीमारी को बढ़ने से रोकता है बल्कि इसे जड़ से ठीक भी करता है।

urticaria ka ilaaj
रेणुका बहन श्रीमाली की प्रेरणादायक कहानी: 10 साल की तकलीफ से छुटकारारेणुका बहन श्रीमाली पिछले 10 वर्षों से एक गंभीर समस्या से जूझ रही थीं। उन्हें जब भी कुछ खाने की कोशिश करतीं, उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और अत्यधिक खुजली होने लगती थी। इस समस्या के कारण वे बहुत परेशान थीं और 10 वर्षों तक कुछ भी सही तरीके से नहीं खा पाती थीं। उन्होंने कई जगहों पर इलाज कराया, लेकिन कोई भी उपचार कारगर नहीं हुआ।
ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर से नई उम्मीदआखिरकार, 17 मई 2021 को उन्होंने ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में अपना ट्रीटमेंट शुरू किया। पहले से निराश हो चुकीं रेणुका बहन के लिए यह एक नई उम्मीद की किरण थी।एक साल में चमत्कारी सुधारट्रीटमेंट शुरू करने के बाद, धीरे-धीरे उनके स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होने लगा। एक साल के भीतर उन्होंने अपने आहार में वे सभी चीजें फिर से शुरू कर दीं, जिन्हें वे पहले नहीं खा पाती थीं। पहले जहाँ कोई भी चीज खाने से उनका शरीर फूल जाता था और खुजली होती थी, वहीं अब वे बिना किसी परेशानी के सामान्य जीवन जी रही हैं।ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर का योगदान
रेणुका बहन का कहना है कि यह इलाज उनके लिए किसी चमत्कार से कम नहीं था। उन्होंने अपनी पुरानी जीवनशैली को फिर से अपनाया और अब वे पूरी तरह से स्वस्थ महसूस कर रही हैं। उनके अनुसार, ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में इलाज का असर तुरंत दिखने लगता है और दवाइयाँ भी पूरी तरह से प्रभावी होती हैं।
अन्य समस्याओं के लिए भी कारगर
इस रिसर्च सेंटर में सिर्फ एलर्जी ही नहीं, बल्कि स्पॉन्डिलाइटिस, पीसीओडी जैसी कई अन्य बीमारियों का भी सफलतापूर्वक इलाज किया जाता है। रेणुका बहन जैसी कई अन्य मरीजों को भी यहाँ से सकारात्मक परिणाम मिले हैं।
रेणुका बहन का संदेश
रेणुका बहन उन सभी लोगों को धन्यवाद देती हैं जिन्होंने उनके इलाज में मदद की। वे यह संदेश देना चाहती हैं कि यदि कोई भी व्यक्ति किसी पुरानी बीमारी से परेशान है और अब तक उसे कोई समाधान नहीं मिला है, तो उन्हें ब्रह्म होम्योपैथिक रिसर्च सेंटर में एक बार अवश्य आना चाहिए।
"यहाँ इलाज प्रभावी, सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक तरीके से किया जाता है। मैं इस सेंटर के प्रति आभार व्यक्त करती हूँ, जिसने मुझे 10 साल पुरानी तकलीफ से राहत दिलाई।"
अगर आप भी किसी स्वास्थ्य समस्या से जूझ रहे हैं और समाधान की तलाश में हैं, तो इस होम्योपैथिक उपचार को आज़मा सकते हैं।
Departments
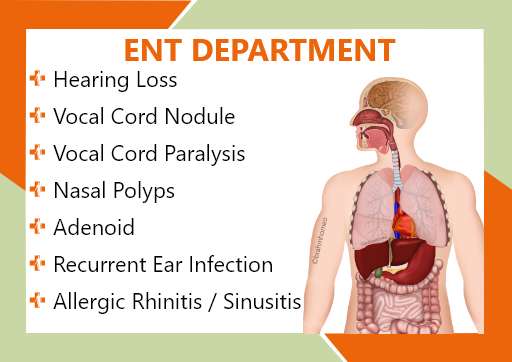
ENT DEPARTMENT
Hearing Loss, Vocal Cord Nodule, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Nasal Polip, Adenoid, Recurrent ear infection, Allergic Rhinitis/Sinusitis

GENERAL MEDICINE
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid Disorders
Cholesterol problem (Dislipimidia)
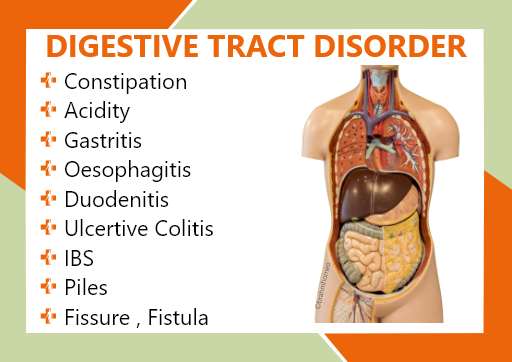
DIGESTIVE TRACT DISORDER
Constipation
Acidity
Gastritis
Oesophagitis
Duodenitis
Ulcertive Colitis
IBS
Piles
Fissure
Fistula
Diseases
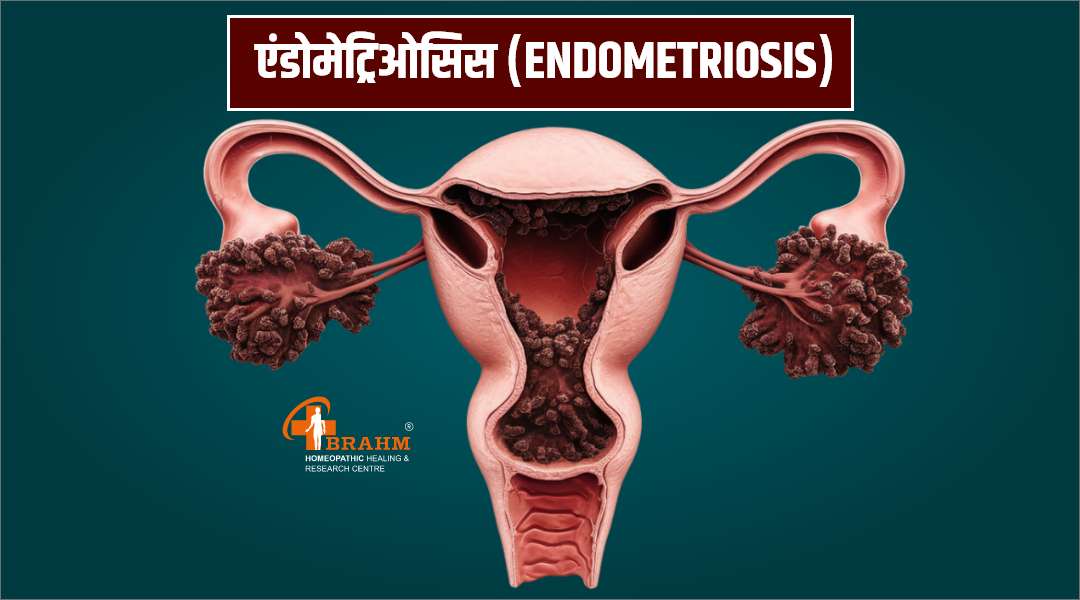
Endometriosis ka homeopathy me ilaaj
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस (Endometriosis)
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस यह एक गंभीर महिला स्वास्थ्य समस्या है जो प्रजनन क्षमता को प्रभावित कर सकती है। एंडोमेट्रिओसिस केवल माहवारी के दर्द का कारण नहीं बनती है, बल्कि यह महिलाओं के जीवन की गुणवत्ता को भी प्रभावित कर सकती है। यह एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें एंडोमेट्रियल ऊतक, जो आमतौर पर गर्भाशय के अंदर होता है, अन्य स्थानों जैसे कि पेट, अंडाशय और अन्य अंगों पर विकसित हो जाता है। आज इस वीडियो में, हम एंडोमेट्रिओसिस के कारणों, लक्षणों, निदान, उपचार और प्रबंधन के बारे में चर्चा करेंगे।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस में, गर्भाशय के भीतर मौजूद एंडोमेट्रियल ऊतक, विभिन्न स्थानों पर विकसित होकर सूजन और दर्द का कारण बनता है। जब माहवारी होती है, तो यह ऊतक भी माहवारी के समान प्रतिक्रिया करता है, लेकिन चूंकि यह शरीर के बाहर है, यह रक्त को ठीक से बाहर नहीं निकाल पाता है, जिससे सूजन, कष्ट और अन्य स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ उत्पन्न होती हैं।
इसकी पैथोफिजियोलॉजी में यह भी शामिल होता है कि यह सूजन और ऊतकों के विकास से जुड़े होते हैं, जिन्होंने आसपास के अंगों जैसे अंडाशय, ट्यूब और अन्य विचारित क्षेत्रों को प्रभावित किया।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस के कई संभावित कारण होते हैं:
1. आनुवंशिकी: यदि परिवार में किसी को यह समस्या है, तो महिलाओं में इसका जोखिम बढ़ जाता है। 2. हॉर्मोनल परिवर्तन: एस्ट्रोजेन हार्मोन की अधिकता इस स्थिति को बढ़ा सकती है। 3. सेक्सुअल पाथोलॉजी: स्वस्थ यौन संबंधों की कमी, उदाहरण के लिए, पीरियड के दौरान असामान्य परिवर्तन। 4. मासिक धर्म का रिवर्स फ्लो: कुछ सिद्धांत कहते हैं कि माहवारी के दौरान रक्त गर्भाशय की जगह अन्य स्थानों पर चला जाता है। भारत में, एंडोमेट्रिओसिस की समस्या लगभग 10% प्रजनन आयु की महिलाओं में देखी जाती है।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस के लक्षण इस प्रकार हैं:
1. गंभीर मासिक धर्म का दर्द: जो सामान्य से अधिक भी हो सकता है।
2. अनियमित माहवारी: समय पर नहीं होना या अधिक मात्रा में होना। 3. पेल्विक दर्द: पीठ और पेल्विक क्षेत्र में स्थायी दर्द। 4. मिश्रित समस्याएँ: जैसे कि प्रजनन क्षमता में कमी और गर्भधारण में कठिनाई। 5. पाचन समस्याएँ: जैसे कि कब्ज या दस्त, जो माहवारी के दौरान बढ़ सकते हैं। 6. यौन क्रिया में दर्द: सेक्स के दौरान असुविधा या दर्द का अनुभव होना।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस का निदान करने के लिए निम्नलिखित परीक्षण किए जाते हैं:
1. मेडिकल इतिहास: डॉक्टर आपके लक्षण और पारिवारिक स्वास्थ्य इतिहास के बारे में जानकारी लेते हैं। 2. शारीरिक परीक्षा: पेल्विक परीक्षा द्वारा डॉक्टर स्थिति की पुष्टि करते हैं।
3. इमेजिंग टेस्ट: जैसे कि अल्ट्रासाउंड या MRI, जो समस्या की स्थिति को जानने में मदद करते हैं। 4. लैप्रोस्कोपी: यह एक इन्स्ट्रूमेंट होता है जो पेट के अंदर देखने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।
इन परीक्षणों के आधार पर डॉक्टर एंडोमेट्रिओसिस का निदान करते हैं।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस का प्रोग्नोसिस भिन्न हो सकता है। यदि प्रारंभिक चरण में इसका निदान किया जाता है और उचित उपचार किया जाता है, तो महिलाओं की प्रजनन क्षमता पर सकारात्मक प्रभाव देखने को मिल सकता है।
हालांकि, कुछ मामलों में यह स्थिति कष्टकारी हो सकती है और गंभीर जटिलताओं का कारण बन सकती है, जैसे कि बुनियादी अंगों पर प्रभाव, प्रति माह दर्द, और पेल्विक इंफ्लेमेटरी बीमारी।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस से बचने के लिए कुछ महत्वपूर्ण सुझाव निम्नलिखित हैं:
1. स्वस्थ आहार: फल, सब्जियाँ, और ओमेगा-3 फैटी एसिड से भरपूर खाद्य पदार्थों का सेवन करें। 2. नियमित व्यायाम: शारीरिक गतिविधि को बनाए रखें, जो हार्मोन को संतुलित करने में मदद करती है। 3. तनाव प्रबंधन: ध्यान, योग, या अन्य आराम करने वाली गतिविधियों का समावेश करें। 4. नियमित स्वास्थ्य जांच: समय-समय पर अपने स्वास्थ्य का मूल्यांकन कराएँ।
एंडोमेट्रिओसिस के लिए होम्योपैथिक उपचार में कुछ मुख्य दवाएँ प्रभावी हो सकती हैं:
1. सिलिका: यदि आपकी स्थिति व्यथित होती है और आप स्थायी दर्द का अनुभव करते हैं। 2. पल्सेटिला: जब दर्द मासिक धर्म के समय बढ़ता है। 3. लैकेनियम: पीरियड्स के दौरान दर्द के लिए। ब्रह्म होमियोपैथी एक आधुनिक पद्धति पर आधारित चिकित्सा केंद्र है, जहाँ इलाज केवल लक्षणों का नहीं, बल्कि बीमारी की जड़ का किया जाता है। यहाँ रोगियों को बिना किसी साइड इफेक्ट के सुरक्षित और प्रभावशाली होम्योपैथिक उपचार प्रदान किया जाता है। आधुनिक तकनीक और गहरी अनुभवशीलता के साथ, ब्रह्म होमियोपैथी हर मरीज को व्यक्तिगत ध्यान और विश्वास के साथ इलाज देता है। यदि आप सुरक्षित और भरोसेमंद इलाज की तलाश में हैं, तो ब्रह्म होमियोपैथी आपके स्वास्थ्य की राह में एक विश्वसनीय साथी है।

asd treatment in homeopathy
ऑटिज़्म स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डरऑटिज़्म स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डर, जिसे हम संक्षेप में ASD कहते हैं। -ASD एक जटिल न्यूरोडेवलपमेंटल विकार है जो व्यक्ति की संवेदी, सामाजिक, और व्यवहारिक क्षमताओं को प्रभावित करता है। -इसकी पैथोफिजियोलॉजी, कारण, लक्षण, निदान, पूर्वानुमान, रोकथाम, और होम्योपैथिक प्रबंधन। साथ ही, हम भारत में इसके आंकड़ों और इसके सामाजिक प्रभाव पर भी गौर करेंगे। ऑटिज़्म स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डर (ASD) एक न्यूरोडेवलपमेंटल विकार है जो संचार, सामाजिक इंटरैक्शन, और व्यवहार में विभिन्न बाधाओं के साथ आता है। ASD की विशेषताएँ वैरिएटिव होती हैं, यानी हर व्यक्ति की स्थिति अलग हो सकती है। ASD को विभिन्न प्रकारों में वर्गीकृत किया गया है:- क्लासिक ऑटिज़्म (कनर्वटिव ऑटिज़्म): जिसमें गंभीर संचार और सामाजिक व्यवहार की कमी होती है।- असपर्जर सिंड्रोम: जिसमें व्यक्ति की आईक्यू सामान्य होती है, लेकिन सामाजिक स्किल्स कमजोर होती हैं।- पर्वासिव डेवलपमेंटल डिसऑर्डर (PDD): जो अन्य कम स्पष्ट ऑटिज़्म संबंधी स्थितियों को कवर करता है।आँकड़े (भारत में):आँकड़े (भारत में):- विश्व स्वास्थ्य संगठन (WHO) के अनुसार, भारत में 1 से 2% बच्चे ASD से प्रभावित हो सकते हैं।- 2018 की एक रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, भारत में लगभग 5 मिलियन लोग ऑटिज़्म स्पेक्ट्रम डिसऑर्डर से प्रभावित हैं। * न्यूरोट्रांसमीटर असंतुलन * - - मस्तिष्क में न्यूरोट्रांसमीटर, जैसे कि सेरोटोनिन और डोपामाइन, का असंतुलन ASD के लक्षणों को प्रभावित कर सकता है। ये पदार्थ संवेदी प्रक्रियाओं और सामाजिक व्यवहार में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं। * मस्तिष्क की संरचना: *
-ऑटिज़्म से प्रभावित व्यक्तियों में मस्तिष्क के कुछ हिस्सों, जैसे कि अमिग्डाला और प्रीफ्रंटल कॉर्टेक्स, में विकास संबंधी समझौता देखा गया है। यह भावनाओं के प्रबंधन और सामाजिक व्यवहार में मुश्किलों का कारण बनता है।
* जीन संबंधी कारक: *
- परिवारिक इतिहास और आनुवंशिकता भी ASD के विकास में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं। कुछ विशेष जीनों का ऑटिज़्म के साथ संबंध पाया गया है। * पर्यावरणीय कारक: *
- गर्भावस्था में धूम्रपान, जन्म के समय किसी तरह का तनाव, और वास्तव में शुरुआती विकास में होने वाले ऑक्सीजन की कमी भी इसकी संभावनाओं को बढ़ा सकते हैं।
ASD के कई संभावित कारण होते हैं, जिनमें शामिल हैं:जेनेटिक कारक:- यदि परिवार में किसी सदस्य को ASD है, तो अन्य सदस्यों के इस विकार से ग्रस्त होने की संभावना अधिक होती है। पर्यावरणीय कारक: - गर्भावस्था में विषाक्त पदार्थों के संपर्क, जैसे कि भारी धातुएं और रासायनिक पदार्थ, भी ASD के विकास में योगदान कर सकते हैं।मनोवैज्ञानिक कारक:- मानसिक स्वास्थ्य समस्याएं, जैसे कि अवसाद और चिंता, भी ASD के जोखिम को बढ़ा सकती हैं। मस्तिष्क विकास में समस्याएं: - गर्भावस्था में संक्रमण, जैसे कि जर्मन मेजिल्स या सिटोमेगालोवायरस, मस्तिष्क के विकास को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं।
ASD के लक्षण मुख्य रूप से तीन श्रेणियों में विभाजित होते हैंसामाजिक इंटरैक्शन में कठिनाई: - आंखों में संपर्क से बचना। - सामाजिक संकेतों का सही तरह से समझने में कठिनाई। संवेदी प्रोसेसिंग में असामान्यताएँ: - कुछ व्यक्तियों को तेज आवाज़ों, रोशनी, और विशेष वस्तुओं के प्रति संवेदनशीलता हो सकती है। - अपनी पसंद की गतिविधियों और वस्तुओं पर अत्यधिक ध्यान केंद्रित करना।
" style="width:100%;">
सामान्य लक्षण- समय पर नहीं बोलना।- सामाजिक खेलों में रुचि नहीं होना।- असामान्य तरीके से हँसना या रोना।- निश्चित नियमों और रूटीन का पालन करना। ASD का निदान निम्नलिखित प्रक्रियाओं के माध्यम से किया जाता हैमेडिकल इतिहास और शारीरिक जांच:- डॉक्टर बच्चे के विकासात्मक इतिहास, शारीरिक स्वास्थ्य और व्यवहार की समस्याओं का मूल्यांकन करते हैं। मानसिक स्वास्थ्य मूल्यांकन: - मान्यता प्राप्त परीक्षणों और प्रश्नावली का उपयोग करके ASD के लक्षणों की गंभीरता का अध्ययन किया जाता है। स्कूल रिपोर्ट और शिक्षक की जानकारी:- स्कूल में बच्चे के व्यवहार और प्रदर्शन के आधार पर शिक्षक की प्रतिक्रियाएँ भी महत्वपूर्ण होती हैं।
ASD का प्रोग्नोसिस कई कारकों पर निर्भर करता हैउपचार की प्रभावशीलता: - सही समय पर उपचार, जैसे कि चिकित्सा और व्यवहार प्रबंधन, से जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार हो सकता है। समय पर निदान: - जल्दी निदान और उचित सहायता से व्यक्ति की सामाजिक और संचार संबंधी क्षमताएँ बेहतर हो सकती हैं। समर्थन प्रणाली: - परिवार और दोस्तों का समर्थन भी व्यक्ति की मानसिक स्वास्थ्य में सकारात्मक प्रभाव डाल सकता है। विकृति: - किसी व्यक्ति के जीवन में ASD का प्रभाव देखी गई विभिन्न उम्र में अलग-अलग हो सकता है, जो उनके व्यक्तिगत अनुभवों पर निर्भर करता है।
" style="width:100%;">ASD की रोकथाम के लिए कुछ उपाय किए जा सकते हैंस्वस्थ गर्भावस्था: - गर्भवती महिलाओं को धूम्रपान और शराब का सेवन नहीं करना चाहिए और उचित पोषण का ध्यान रखना चाहिए। मनोवैज्ञानिक समर्थन: - माता-पिता को मानसिक स्वास्थ्य के प्रति जागरूक रहना चाहिए और आवश्यकता पड़ने पर पेशेवर सहायता प्राप्त करनी चाहिए। स्कूली शिक्षा: - स्कूलों में ऑटिज़्म संबंधित जागरूकता कार्यक्रम संचालित करना, जिससे शिक्षक और विद्यार्थी इस विकार के प्रति संवेदनशील बन सकें। बच्चों के लिए गतिविधियाँ: - बच्चों को सामाजिक खेलों और अन्य तैयारियों में शामिल करना जो उनकी सामाजिक क्षमताओं को बढ़ा सके।

obsessive compulsive disorder treatment
ऑब्सेसिव-कंपल्सिव डिसऑर्डर (OCD) क्या है?(OCD) (ऑब्सेसिव-कंपल्सिव डिसऑर्डर एक मानसिक विकार है जिसमें व्यक्ति को प्रारंभिक रूप से अकारण और अवांछित विचारों (ऑब्सेशन) से ग्रस्त होना पड़ता है। ये विचार व्यक्ति के मन में बार-बार आते हैं और उन्हें चिंता और तनाव का सामना करना पड़ता है।
इन विचारों को तनाव से राहत पाने के लिए व्यक्ति कई बार कुछ विशेष कार्य करने के लिए मजबूर होता है, जैसे कि हाथ धोना, चीजों को निश्चित तरीके से रखना, या बार-बार जांचना।
आंकड़े (भारत में):
- भारत में लगभग 5% से 3% जनसंख्या OCD से प्रभावित है। - मानसिक स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं में OCD का योगदान 12% का है, जो इसे एक महत्वपूर्ण विकार बनाता है। OCD के पीछे की जैविक और मनोवैज्ञानिक प्रक्रिया का अध्ययन करने पर हम कुछ जटिल तत्वों को पाते हैं
* न्यूरोट्रांसमीटर असंतुलन *
- मस्तिष्क में सेरोटोनिन की कमी या असंतुलन से OCD के लक्षणों को बढ़ा सकता है। सेरोटोनिन मस्तिष्क में भावनाओं और व्यवहारों को कण्ट्रोल में रखने में मदद करता है।
* मस्तिष्क की संरचना *
- OCD से प्रभावित व्यक्तियों में मस्तिष्क के कुछ क्षेत्रों, जैसे कि ऑर्बिटोफ्रंटल कॉर्टेक्स और स्ट्रिएटम, की संरचना में परिवर्तन होता है। *जीन और आनुवंशिकी*
- यदि परिवार में किसी सदस्य को OCD है, तो अन्य सदस्यों में इसके होने की संभावना और भी बढ़ जाती है। जीन से संबंधित होने वाले कई कारक इसे उच्च जोखिम में डालते हैं। * मनोवैज्ञानिक कारक *
- चिंता , अवसाद, और अन्य मानसिक स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ OCD के विकास में योगदान देती है।
२) OCD के कई संभावित कारण हैं?
OCD के कई कारण है ,जोकि इस प्रकार से है , १) जेनेटिक फैक्टर: - यदि परिवार में कोई व्यक्ति को OCD से परेशान है, तो परिवार के अन्य सदस्यों में भी इसके होने की संभावना अधिक होती है।
२) पर्यावरणीय कारण:- मानसिक या शारीरिक हिंसा का अनुभव, भी OCD को प्रेरित कर सकती हैं। ३) मनोवैज्ञानिक कारण: - व्यक्ति की सोचने की प्रक्रिया और व्यवहार भी OCD को जन्म दे सकते हैं। यह चिंताओं से ही शुरू होता है।
४) मस्तिष्क की असामान्य गतिविधि:- मस्तिष्क के कुछ हिस्सों में अधिक सक्रियता भी OCD के लक्षणों को बढ़ा सकती है।
३)OCD के लक्षणों को मुख्य रूप से दो श्रेणियों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है
१) ऑब्सेशन (Obsessions): - अनियंत्रित, आवर्ती विचार होते हैं जो व्यक्ति को अत्यधिक चिंता और तनाव में डाल देते हैं। २) कंपल्शन (Compulsions):- ऐसे अनिवार्य काम हैं जिन्हें व्यक्ति को चिंता को कम करने के लिए करना पड़ता है।
३) OCD के सामान्य लक्षण - बार-बार हाथ धोना। - चीजों को लगातार सही क्रम में रखना। - वस्तु की जांच करना जैसे कि दरवाज़ा बंद है या नहीं। - गंदगी और संक्रमण के बारे में अत्यधिक चिंता होना।
४) OCD का निदान करने के लिए विभिन्न प्रक्रियाएँ अपनाई जाती हैं?
*मेडिकल इतिहास*
डॉक्टर आप के लक्षणों और पारिवारिक चिकित्सा इतिहास को देखते हैं। * मानसिक स्वास्थ्य मूल्यांकन*
- मानसिक स्वास्थ्य पेशेवर विभिन्न परीक्षणों और प्रश्नावली का उपयोग करते हैं ताकि OCD के लक्षणों की गंभीरता का आकलन किया जा सके।
५ ) OCD का प्रोग्नोसिस कई कारकों पर निर्भर करता है?
# उपचार की प्रभावशीलता
- उचित चिकित्सा और मनोचिकित्सा से सामान्य स्थिति में सुधार संभव है। # नैतिक समर्थन:
- परिवार और दोस्तों का समर्थन मरीजों की मानसिक स्थिति में काफी हद तक सुधार कर सकता है। # समय पर निदान:
- जल्दी निदान और उपचार से जीवन की गुणवत्ता में सुधार होती है।
Videos

acute necrotizing pancreatic ka homeopathy me ilaaj
एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस : कारण, लक्षण और उपचार
एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस (Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis) अग्न्याशय (Pancreas) की एक गंभीर और जानलेवा स्थिति होती है, जिसमें पैंक्रियास की कोशिकाएं नष्ट (Necrosis) होने लगती हैं। यह स्थिति आमतौर पर तीव्र पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के जटिल रूप में विकसित होती है। इसका समय पर और सही इलाज न होने पर संक्रमण, अंग विफलता और मृत्यु तक हो सकती है।
१) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के होने के क्या कारण है?
एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के मुख्य कारणों में शामिल हैं: जैसे की - पित्ताशय की पथरी : – यह पैंक्रियास की नली को अवरुद्ध कर के सूजन और नेक्रोसिस का कारण बनता है।
- अत्यधिक शराब का सेवन
- उच्च ट्राइग्लिसराइड स्तर
- कुछ दवा का साइड इफेक्ट का होना -वायरल संक्रमण
२ ) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने के क्या लक्षण दिखाई देते है ?
इस बीमारी के लक्षण निचे बताये गए अनुसार हो सकते है , जैसे की ,
- पेट के ऊपरी भाग में तेज दर्द का होना - उल्टी और मतली
- तेज धड़कन और बुखार -पेट में सूजन का आ जाना - शरीर में कमजोरी सा लगना
- पेशाब में बदलाव
- सांस लेने में परेशानी
३) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस उपचार क्या है ?
1. अस्पताल में भर्ती या निगरानी : मरीज को ICU में एडमिट किया जाता है। और निगरानी के लिए खून का टेस्ट, CT स्कैन , अल्ट्रासाउंड जाँच भी किए जाते हैं। 2. IV Fluids और पोषण:
- डिहाइड्रेशन न हो और उस से बचाने के लिए IV फ्लूइड्स दिया जाता है।
- खाने-पीने से कुछ दिन तक परहेज कर के शरीर को आराम दिया जाना भी जरुरी होता है।
3. बुखार और दर्द का इलाज:
बुखार और संक्रमण को कम करने या रोकने के लिए एंटीबायोटिक्स भी दिए जाते हैं।
४) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस होने पर क्या देखभाल होनी चाहिए ?
- उबली हुई और कम मसाले वाली चीजें को खाना चाहिए। - धीरे-धीरे लिक्विड डाइट शुरू करें और डॉक्टर के सलाह पर ही ठोस खाना शुरू करें। - शराब और तले-भुने भोजन से पूरी तरह दुरी बनाये रखना चाहिए।
५) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइजिंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस से बचाव के लिए क्या करना चाहिए ?
- समय - समय पर गॉलब्लैडर की पथरी का इलाज करवाए - शराब से दुरी बनाये रखें।
-संतुलित और कम फैट वाली डाइट लें।

ca 19 9 kya hai
CA 19-9 क्या है और इसके बढ़ने से कैंसर का खतरा क्यों हो सकता है?
CA 19-9 (Cancer Antigen 19-9) एक प्रकार का प्रोटीन है, जिसे ट्यूमर मार्कर कहा जाता है। यह शरीर में उन कोशिकाओं द्वारा उत्पादित होता है, जो असामान्य रूप से बढ़ जाती हैं। सामान्यतः, यह प्रोटीन पाचन तंत्र के कुछ अंगों जैसे पैंक्रियाज, जिगर, गल मार्ग, और आंतों में पाया जाता है। जब इन अंगों में कैंसर होता है, तो CA 19-9 का स्तर शरीर में बढ़ सकता है।
यह मार्कर विशेष रूप से पैंक्रियाटिक कैंसर, कोलोन कैंसर, लिवर कैंसर, औरGall bladder (पित्ताशय की थैली) के कैंसर के साथ जुड़ा हुआ है। हालांकि, यह जरूरी नहीं कि CA 19-9 का स्तर बढ़ने का मतलब हमेशा कैंसर ही हो, क्योंकि कई बार यह संक्रमण, सूजन, या अन्य गैर-कैंसर बीमारियों में भी बढ़ सकता है।
CA 19-9 का परीक्षण क्यों किया जाता है?
डॉक्टर इस परीक्षण का उपयोग मुख्य रूप से निम्नलिखित उद्देश्यों के लिए करते हैं:
- **कैंसर का निदान:** कोई मरीज के लक्षण यदि कैंसर से मिलते-जुलते हैं, तो CA 19. 9 का जाँच कर पता लगाया जा सकता है कि मरीज को कैंसर या नहीं है।
- **कैंसर का प्रगति ट्रैकिंग:** यदि पहले से कैंसर का निदान हो चुका है, तो इस मार्कर का स्तर उसकी प्रगति या उपचार की प्रतिक्रिया को समझने में मदद करता है।
- **रिसिडिव (पुनः उत्पन्न) कैंसर की जांच:** इलाज के बाद यदि CA 19-9 का स्तर फिर से बढ़ता है, तो इसका मतलब हो सकता है कि कैंसर वापस आ गया है।
CA 19-9 का स्तर कितना होना चाहिए?
CA 19-9 का नार्मल लेवल 37 Units per milliliter से नीचे माना जाता है। पर ये लेवल अगर ज्यादा बढ़ जाये तो ,कैंसर या कोई अन्य स्थिति भी हो सकती है।
- **उच्च स्तर:** कैंसर, सूजन, संक्रमण, या जिगर की बीमारी का संकेत हो सकता है। - **बहुत अधिक स्तर:** यह अधिक गंभीर कैंसर के हो सकते हैं, जैसे कि पैंक्रियाटिक कैंसर, विशेष रूप से जब यह बढ़ जाता है।
क्या CA 19-9 का स्तर बढ़ने का मतलब हमेशा कैंसर ही है?
- उत्तर है, नहीं।
यह कोई निश्चित निदान नहीं है। कई गैर-कैंसर स्थितियों में भी इसकी मात्रा बढ़ भी सकती है, जैसे:
- पैंक्रियाटिक सूजन (पैंक्रियाटाइटिस)
- जिगर की बीमारियाँ (जैसे हेपेटाइटिस)
- Gallstones (पित्ताशय की पथरी)
- संक्रमण या सूजन
इसलिए, यदि CA 19-9 का स्तर बढ़ता है, तो इसका मतलब यह नहीं कि व्यक्ति के पास कैंसर है। यह केवल एक संकेत है, जिसके बाद और जांचें की जाती हैं, जैसे कि इमेजिंग (अल्ट्रासाउंड, सीटी स्कैन, MRI) और बायोप्सी, ताकि सही निदान किया जा सके।
CA 19-9 का उपयोग सीमित क्यों है?
क्योंकि बहुत से गैर-कैंसर मामलों में भी CA 19-9 का स्तर बढ़ सकता है, इसलिए यह मार्कर केवल एक सहायता उपकरण है, न कि अंतिम निदान। इसका प्रयोग मुख्य रूप से कैंसर का अनुमान लगाने, उसकी प्रगति का मूल्यांकन करने, और उपचार की प्रतिक्रिया देखने के लिए किया जाता है।
निष्कर्ष
- CA 19-9 एक ट्यूमर मार्कर है, जो मुख्य रूप से पैंक्रियाटिक और अन्य संबंधित अंगों के कैंसर की पहचान में मदद करता है।**
- **इसके स्तर का बढ़ना जरूरी नहीं कि कैंसर ही हो, बल्कि यह संक्रमण, सूजन, या जिगर की बीमारियों का भी संकेत हो सकता है।**
- यह मार्कर केवल निदान में मदद करता है, अंतिम पुष्टि के लिए अन्य टेस्ट जरूरी होते हैं।**

acute necrotizing pancreas ka ilaaj
१)एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास होने के क्या कारण होते है ?
एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास होता है जब हमारे शरीर अग्न्याशय में सूजन या चोट लगती है, और अग्नाशयी एंजाइम लीक होने लग जाते हैं।
यह अग्न्याशय के ऊतक को नुकसान पहुंचाते है। इस क्षति को उलटा नहीं किया जा सकता है, तो यह नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस का कारण बनते है। कुछ मामलों में, ऊतक संक्रमित हो सकते हैं। यह बैक्टीरिया से होता है जो की मृत ऊतक में फैल जाते हैं।
** एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास होने का कारण इस प्रकार से होता है जैसे की , - जयदा दवा का उपयोग करना - खून में कैल्सियम का स्तर ज्यादा होना , - पित्ताशय की पथरी होना , - बहुत ज़्यादा शराब पीना
२) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास का खतरा किसे होता है?
आपको कोई स्वास्थ्य की समस्या है जो की अग्नाशयशोथ का कारण बन सकती है, तो आपको एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस का जोखिम अधिक हो सकता है। इसमें पित्त पथरी शामिल है।
आप अपनी स्वास्थ्य स्थिति का इलाज करके एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियाटाइटिस के जोखिम को कम भी कर सकते हैं। जिसमे कम शराब पीने से भी आपका जोखिम कम हो सकता है।
3) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास में वजन नही बढ़ने का क्या कारण है ?
एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैन्क्रियाटाइटिस में वजन न बढ़ने का कारण निचे अनुसार हो सकते है ,जैसे की , -पाचन की कमी होने से -संक्रमण और सूजन का होना -पोषण की कमी
-विटामिन की कमी
४) एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास होने पर क्या लक्षण होते है?
एक्यूट नेक्रोटाइज़िंग पैंक्रियास होने के लक्षण निचे बताया गया है ,जो की इस प्रकार से है , - पेट के ऊपरी भाग में दर्द होता है और यह दर्द धीरे-धीरे बढ़ता जाता है। - पेट का ऊपरी हिस्सा सूजा हुआ लगना -मतली और उल्टी का होना - हृदय की गति का तेज हो जाना
